
Table of Contents
Embarking on a nursing dissertation is a significant undertaking, and the journey begins with a robust and well-articulated proposal for nursing dissertation. This document serves as your roadmap, outlining your research intentions and persuading your committee of the viability and significance of your study. It’s not merely a formality; it’s a crucial step that sets the foundation for a successful and impactful dissertation. A meticulously crafted proposal for nursing dissertation can mean the difference between a smooth research process and one riddled with obstacles.
This article aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to develop a compelling and convincing proposal for nursing dissertation.
Understanding the Purpose of a Proposal for Nursing Dissertation
Before diving into the specifics, it’s essential to understand the fundamental purpose of your proposal for nursing dissertation. This document aims to:
- Demonstrate Research Competence: It showcases your understanding of research methodologies, your critical thinking skills, and your ability to design a sound study.
- Articulate a Clear Research Problem: You need to identify a gap in the existing literature, demonstrating a clear rationale for your research. This is why the foundation of a strong proposal for nursing dissertation is a well-defined problem statement.
- Outline Your Research Plan: The proposal details your proposed methods, data collection techniques, and analysis plans, demonstrating a clear path to answering your research questions.
- Secure Committee Approval: Ultimately, the proposal for nursing dissertation needs to convince your faculty committee that your research is feasible, relevant, and ethically sound.
- Provide a Framework for Your Study: The approved proposal for nursing dissertation serves as a guiding document throughout your research, keeping you focused and on track.

Key Components of a Proposal for Nursing Dissertation
A typical proposal for nursing dissertation contains several core components. While specific requirements may vary across institutions, the following sections are generally expected:
1. Title:
Your title should be concise, informative, and reflective of your research topic. It should capture the essence of your study and be clear enough for someone to grasp its central focus immediately. A strong title for your proposal for nursing dissertation sets a positive first impression.
2. Abstract:
This is a brief summary of your entire proposal. It should succinctly outline your research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. The abstract acts as a mini-version of your proposal for nursing dissertation and serves as the first point of contact with your readers.
3. Introduction:
The introduction provides the context for your research. It should introduce your topic, establish its significance within the field of nursing, and clearly state your research problem or question. This section needs to justify why this particular research is important and necessary, thereby making the proposal for nursing dissertation convincing.
- Background: Provide relevant background information on the chosen topic. Briefly review the existing literature and explain its importance to nursing practice and patient care.
- Problem Statement: Clearly articulate the gap in knowledge or the issue you intend to address. This is a crucial part of the proposal for nursing dissertation, as it justifies the need for your research.
- Research Question(s) or Hypotheses: State your research questions or hypotheses clearly and concisely. These should directly relate to your problem statement and guide your entire research process. A well-defined question is central to a strong proposal for nursing dissertation.
4. Literature Review:
This section provides a comprehensive overview of existing research related to your topic. It demonstrates your understanding of the current state of knowledge and identifies gaps that your study will address. A robust literature review is integral to any well-structured proposal for nursing dissertation.
- Synthesis and Critique: Go beyond summarizing individual studies. Analyze the literature, identify themes, contradictions, and limitations, and clearly explain where your research fits within this context.
- Relevance: Demonstrate how the existing literature relates to your research problem and question. Highlight the contributions that your study will make to the field. This section showcases the rationale behind your proposal for nursing dissertation.
5. Theoretical Framework:
This section identifies and explains the theoretical lens or framework that will guide your research. This framework should be relevant to your topic and help in understanding the phenomena you’re investigating. The theoretical framework is essential in supporting the research within a proposal for nursing dissertation.
- Justification: Explain why you have selected a particular theoretical framework and how it will inform your methodology and analysis.
- Application: Discuss how the chosen framework will be applied to your specific research question.
6. Methodology:
This is perhaps the most crucial section of your proposal for nursing dissertation. It details the procedures you will use to gather and analyze data. A clear and well-defined methodology section is critical for gaining approval.
- Research Design: Specify your research design (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods). Justify your choice based on your research question and the nature of the problem.
- Participants/Subjects: Describe your target population, how you plan to recruit them, and any inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Data Collection Methods: Outline the specific methods you will use to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations, existing data). Explain your choices and their suitability for your research question.
- Data Analysis Methods: Describe how you will analyze the data you collect. If using quantitative methods, specify statistical procedures. If using qualitative methods, describe your approach to data analysis (e.g., thematic analysis, grounded theory). A well-thought-out methodology is the backbone of a robust proposal for nursing dissertation.
7. Ethical Considerations:
Address the ethical issues associated with your research. This includes obtaining informed consent, protecting participant confidentiality, and addressing any potential risks to participants. A thorough discussion of ethical aspects is paramount in a proposal for nursing dissertation.
- Informed Consent: Explain how you will obtain informed consent from participants.
- Confidentiality: Detail how you will ensure the confidentiality and anonymity of participants.
- Institutional Review Board (IRB): Describe your plans to seek approval from your institutional review board (or equivalent).
8. Timeline:
Provide a realistic timeline for completing your research, including each stage from data collection to writing your dissertation. A well-planned timeline within your proposal for nursing dissertation demonstrates preparedness.
9. Budget (if applicable):
If your research involves significant costs, outline your anticipated expenses. This may include costs related to travel, materials, or incentives.
10. Dissemination Plan:
Briefly describe how you plan to share your findings (e.g., through publications, presentations at conferences, or professional presentations). Considering the dissemination strategy in your proposal for nursing dissertation is crucial for its wider impact.
11. References:
Include a complete list of all references cited in your proposal. Use a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). Proper referencing is an essential element of any scholarly proposal for nursing dissertation.
Tips and Strategies for Crafting a Winning Nursing Dissertation Proposal
- Start Early: Don’t wait until the last minute to develop your proposal for nursing dissertation. Starting early will give you sufficient time to develop a clear and well-articulated document.
- Seek Feedback: Share your proposal with your faculty advisor and peers to get their feedback. Multiple revisions based on constructive criticism are key.
- Be Specific and Focused: Avoid being too broad or vague. Clearly define your research question, objectives, and methods.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Avoid jargon and complex sentences. Aim for clear, professional, and accessible language.
- Justify Your Choices: For every decision you make, provide a rationale based on the research literature, your theoretical framework, and ethical considerations.
- Proofread Carefully: Ensure that your proposal is free from grammatical errors and typos. A polished and error-free document will make a more favorable impression.
- Align With Your Advisor’s Expectations: Understand your advisor’s preferences and research interests and tailor your proposal for nursing dissertation accordingly.
- Demonstrate Feasibility: Ensure that your proposed research is realistic and achievable within the given timeframe and resources.
- Highlight Your Unique Contribution: Explain how your research will contribute to the field of nursing and advance the knowledge base.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in a Proposal for Nursing Dissertation
Embarking on a nursing dissertation is a significant undertaking, and the journey begins with a robust and well-crafted proposal. The proposal for nursing dissertation serves as a blueprint, outlining the research question, methodology, and anticipated contributions to the field. However, many aspiring nurse researchers stumble along the way, falling into common pitfalls that can derail their projects before they even truly begin. Understanding these potential issues and proactively addressing them is crucial for a successful dissertation experience.
Poorly Defined Research Questions
Often, students start with broad, vague concepts, making it difficult to narrow their focus and develop a clear, testable research plan. For instance, instead of investigating “stress among nurses,” a more refined question might explore, “What is the impact of mandatory overtime on burnout rates among registered nurses in acute care settings?” To avoid this, spend ample time researching existing literature to identify gaps and formulate specific questions that are both feasible and impactful. A good research question is SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
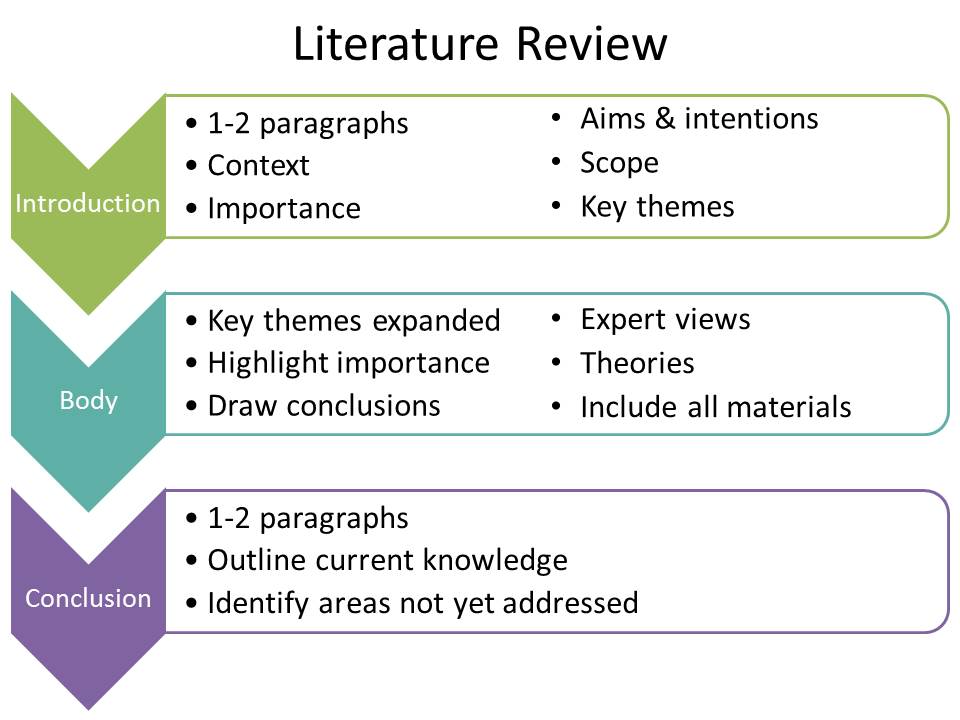
Inadequate Literature Review
A comprehensive literature review is not just a summary of what’s already been written; it’s a critical analysis that establishes the context for your research, highlights the need for your project, and demonstrates your understanding of the theoretical landscape. Students often fail to synthesize information effectively, leading to a disjointed narrative that does not support the proposed research. To overcome this, focus on critical reading. Engage with the literature by identifying recurring themes, analyzing methodological approaches, and noting areas where research is lacking. Avoid simply listing studies; synthesize their findings into a coherent argument.
Unsuitable Methodology
Students may choose research methods that are inappropriate for their research question or lack the expertise to implement correctly. For example, a qualitative research question requires qualitative research methods, and vice versa. Choosing a complicated quantitative study without proper statistical knowledge may doom your project from the start. To avert this, clearly outline your research question and identify the methodological framework that best suits it. Consult with your faculty advisor to ensure feasibility, ethical soundness, and alignment with your expertise. Also, include a detailed description of data collection and analysis techniques.
Lack of Feasibility
Ambitious projects are often attractive, but an overambitious project can be disastrous if it exceeds the time, resources, or expertise available. A well-written proposal for nursing dissertation must demonstrate the project’s practicality. Before submitting your proposal, carefully assess the resources required for data collection, data analysis, and write-up. Consider whether the timescale you’ve set is realistic, and if you have access to participants and required equipment. It’s far better to execute a smaller project thoroughly than to attempt a vast undertaking and produce a rushed, unsatisfactory outcome.
A Weak Theoretical Framework
A strong theoretical framework helps structure your research and provides a lens through which to interpret your findings. It should be clearly explained and directly linked to your research question and methodology. Avoid selecting a framework just to fill a gap; your framework needs to logically connect with the subject matter. Consider how it fits into the wider discipline of nursing and how it can be applied to your study. Neglecting a theoretical framework can lead to poorly interpreted data and a lack of grounding.
Poor Writing and Organization
A disorganized, grammatically flawed proposal for nursing dissertation is difficult to understand and can create a negative impression, no matter how strong the underlying research idea is. To mitigate this, edit and proofread carefully. Follow the specific formatting guidelines provided by your institution and ensure logical flow between different sections. Seek feedback from peers, and revise your work diligently to ensure clarity and precision.
Writing a successful proposal for nursing dissertation requires careful planning, rigorous research, and effective communication. By understanding the common pitfalls— poorly defined research questions, inadequate literature review, unsuitable methodology, lack of feasibility, weak theoretical frameworks, and poor writing—and actively working to avoid them, you can build a solid foundation for a meaningful and impactful nursing dissertation. Remember that the proposal is not just a formality; it is an opportunity to showcase your research potential and pave the way for a successful and rewarding academic experience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nursing Dissertation Proposals
Embarking on a nursing dissertation is a significant undertaking, and the journey begins with a well-crafted proposal. Many students find this initial stage daunting, leading to a flurry of questions. This section addresses some frequently asked questions surrounding the proposal for nursing dissertation, helping to demystify the process and pave the way for a successful research project.
Q: What exactly is a proposal for nursing dissertation?
A: Simply put, a proposal for nursing dissertation is a detailed plan outlining your proposed research. It’s a roadmap that demonstrates to your supervisors that you have a feasible, worthwhile, and methodologically sound research idea. It’s not just a summary; it’s a persuasive document arguing for the importance and feasibility of your project. It needs to showcase your understanding of existing literature and demonstrate how your research will contribute to the field of nursing.
Q: How long should a proposal for nursing dissertation be?
A: Length can vary depending on your university’s specific guidelines. However, generally, a proposal ranges from 1,500 to 3,000 words. It’s crucial to check your department’s requirements, as adhering to specified word counts and formatting is critical. Focus on quality rather than quantity; ensure every section is concise, clear, and purposeful.
Q: What key elements must a proposal for nursing dissertation include?
A: While specifics may differ, most proposals include these essential components:
- Introduction: Briefly introduces your research topic and its significance in the nursing field.
- Literature Review: Summarizes existing research on your chosen topic, highlighting gaps or areas needing further investigation.
- Research Questions/Hypotheses: Clearly states the questions your research aims to answer or the hypotheses you intend to test.
- Methodology: Explains the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques you plan to use.
- Ethical Considerations: Outlines how you will address ethical concerns related to your research (e.g., informed consent, confidentiality).
- Timeline: Provides a realistic timeframe for completing each phase of the research.
- References: Lists all sources cited in your proposal.
- Budget (sometimes required): Outlines expected costs for data collection, analysis, etc.

Q: How do I choose a suitable research topic for my proposal for nursing dissertation?
A: This is often the trickiest part. Choose a topic that genuinely interests you and aligns with your passion for nursing. Consider issues you have encountered in your practice, identify gaps in existing research, or explore emerging areas within the field. Ensure your topic is manageable within the timeframe and resources available. It’s wise to brainstorm, consult with your supervisors, and thoroughly research potential topics before finalizing one. A strong connection between your interests and the chosen topic will make the whole research journey more engaging and successful.
Q: What makes a proposal for nursing dissertation strong?
A: A strong proposal for nursing dissertation demonstrates clarity, feasibility, and significance. Your chosen topic should be well-justified, based on a sound understanding of the existing literature. Your methodology should be appropriate and robust, and your research questions should be clearly articulated and achievable. A strong proposal also showcases meticulous planning and attention to detail. Seek feedback from your supervisors and peers to refine and strengthen your work before submission. Remember, it’s your chance to demonstrate your ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge. It is crucial to get it right!
Final Thoughts
A well-crafted proposal for nursing dissertation is not just a formality but a crucial foundation for successful research. By carefully planning, understanding the key components, and following the tips outlined in this article, you can increase your chances of having your proposal approved and setting yourself up for a rewarding and impactful dissertation journey. Remember that your proposal for nursing dissertation is your roadmap – it will guide you through the complexities of your research and ultimately lead you to a successful outcome. Therefore, invest time and effort in creating a comprehensive, well-articulated, and convincing proposal for nursing dissertation.
The clarity and quality of your proposal for nursing dissertation significantly affect the trajectory of your research, making it a worthwhile investment of your time and effort. Approaching the creation of your proposal for nursing dissertation methodically and thoughtfully will not only impress your committee but also lay a robust foundation for your dissertation success.
Hire Professional Nursing Dissertation Proposal Writing Service
Are you stuck with writing a proposal for nursing dissertation? Then, engage the experts at PhD Nurse Writer. We can help you with crafting an authentic and compelling nursing dissertation proposal, tailored to your specific instructions and needs. Our service covers proposal writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Besides, we also offer help with research papers, essays and case studies.





