Table of Contents
The journey towards a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is an intellectual marathon, a profound exploration into a specific niche of knowledge. At the heart of this demanding yet rewarding endeavour lies the thesis – a substantial piece of original research that contributes new insights to your field. But before a single chapter is fully penned, before the intricate arguments are meticulously woven, there must be a blueprint. This blueprint, the PhD thesis outline, is arguably one of the most critical yet sometimes underestimated components of successful doctoral research.
A well-crafted PhD thesis outline is not merely a list of topics; it is the structural skeleton, the logical roadmap, and the strategic compass that guides your entire research and writing process. Without a robust PhD thesis outline, the vast and complex undertaking of a PhD can quickly become overwhelming, leading to disorganised thoughts, wasted effort, and a final product that lacks coherence and impact.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the art and science of crafting a robust PhD thesis outline. We will explore its purpose, its essential components, a step-by-step approach to its creation, and tips for ensuring it serves as a dynamic and effective tool throughout your doctoral candidacy. Understanding how to develop a strong PhD thesis outline can transform your PhD journey from a daunting mountain to a series of manageable, conquerable hills.
Laying the Groundwork: Prerequisites for Your PhD Thesis Outline
Before you can effectively sit down to craft your PhD thesis outline, certain foundational elements must be in place. Attempting to create an outline without this groundwork is like trying to draw a map of an unexplored territory – you’ll be operating on assumptions rather than knowledge.
- Thorough Literature Review (Preliminary): You need a strong grasp of the existing research in your field. This involves:
- Identifying key theories, concepts, and seminal works.
- Understanding the current state of knowledge and ongoing debates.
- Critically evaluating existing studies, noting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Crucially, identifying the gap(s) in the literature that your research aims to fill. This gap is the justification for your PhD.
- Clearly Defined Research Question(s) and Objectives: Your entire thesis will revolve around answering your research question(s). These questions must be:
- Specific: Not too broad or vague.
- Measurable (or at least assessable): You need to be able to determine if you’ve answered them.
- Achievable: Within the scope of a PhD and your resources.
- Relevant: To your field and the identified gap.
- Time-bound (implicitly): Feasible within the PhD timeframe.
Your objectives are the specific steps you will take to answer these questions. These questions and objectives will directly inform the structure of your PhD thesis outline.
- Understanding Your Methodological Approach: You should have a clear idea of how you will conduct your research. This includes:
- Your research paradigm (e.g., positivism, interpretivism, pragmatism).
- Your research design (e.g., experimental, survey, case study, ethnographic).
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews, questionnaires, archival research, lab experiments).
- Your proposed data analysis techniques.
Your methodology will form a significant chapter in your thesis, and its planned structure needs to be part of your PhD thesis outline.
- Preliminary Data (If Applicable and Possible): For some disciplines, especially in the sciences, some preliminary data collection or pilot studies might have already occurred. This initial data can help shape your research direction and, consequently, your PhD thesis outline.
- Initial Consultation with Supervisor(s): Your supervisor is your primary guide. Discuss your initial ideas, research questions, and proposed scope with them. Their early input can save you considerable time and effort and ensure your PhD thesis outline starts on the right track.
With these foundational elements in place, you are well-equipped to begin the process of constructing a meaningful and robust PhD thesis outline.
The Anatomy of a Robust PhD Thesis Outline: Key Components
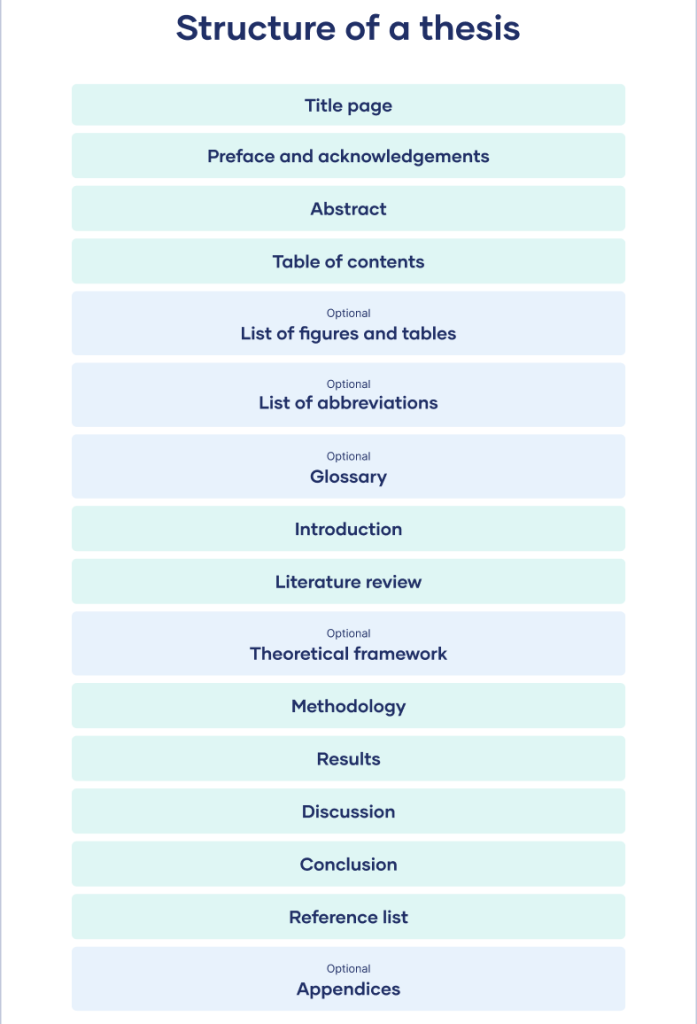
While the exact structure of a PhD thesis can vary depending on the discipline (e.g., humanities often differ from STEM fields), most theses follow a broadly similar pattern. Your PhD thesis outline should reflect this structure, detailing the content planned for each section.
Here’s a common breakdown of thesis components and what your PhD thesis outline might include for each:
- Title Page: (Provisional title – your outline doesn’t need to detail this beyond a placeholder).
- Abstract: (A placeholder in the outline, but the key arguments and findings you intend to present should be reflected in the body of the PhD thesis outline).
- Acknowledgements: (Not a structural part of the research content).
- Table of Contents: (This will be generated from your detailed PhD thesis outline).
- List of Figures/Tables: (Will be generated as you write and populate your thesis).
Core Chapters for Your PhD Thesis Outline:
- Introduction Chapter: This chapter sets the stage for your entire thesis. Your PhD thesis outline for this section should detail:
- Background and Context: What broad area does your research fit into? What information does the reader need to understand the importance of your work?
- Problem Statement/Rationale: Clearly articulate the problem your research addresses or the gap it aims to fill. Why is this research necessary?
- Research Question(s) and/or Hypotheses: State these explicitly.
- Aims and Objectives: What do you aim to achieve, and what specific objectives will guide your research?
- Scope and Limitations of the Study: Define the boundaries of your research. What will it cover, and what will it not cover? Acknowledge any inherent limitations.
- Significance/Contribution of the Study: How will your research contribute to knowledge, theory, practice, or policy? What is its originality?
- Thesis Structure (Roadmap): Briefly outline the organisation of the subsequent chapters. The introduction’s section of the PhD thesis outline is foundational.
- Literature Review Chapter(s): This section demonstrates your mastery of the field and situates your research within existing scholarship. Your PhD thesis outline here needs to be more than just a list of authors.
- Organisation: Will it be thematic, chronological, or methodological? Thematic is often preferred for showing conceptual understanding.
- Key Themes and Debates: Identify the major theoretical frameworks, concepts, and ongoing discussions relevant to your topic.
- Critical Analysis: Outline how you will critically evaluate the literature, not just summarise it. What are the strengths, weaknesses, and contradictions in existing work?
- Identifying the Gap: Clearly show how your review leads to the identification of the specific gap your research will address. This section of the PhD thesis outline proves the necessity of your work.
- Conceptual Framework (if applicable): Outline the framework that will guide your study, derived from the literature.
- Methodology Chapter: This chapter explains how you conducted your research and why your chosen methods are appropriate. Your PhD thesis outline for methodology must be precise and justify your choices.
- Research Philosophy/Paradigm: Briefly state and justify your philosophical stance (e.g., positivist, interpretivist).
- Research Design: Detail your overall strategy (e.g., experimental, case study, ethnography, action research). Justify its suitability for answering your research questions.
- Population and Sampling (if applicable): Describe your target population, sampling strategy, and sample size.
- Data Collection Methods:
- Specify instruments (e.g., survey questionnaires, interview guides, observation protocols).
- Detail procedures for data collection.
- Data Analysis Techniques: Explain the specific methods you will use to analyse your data (e.g., statistical tests, thematic analysis, discourse analysis). Justify these choices.
- Ethical Considerations: Outline the ethical issues relevant to your study and how you addressed them (e.g., informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality).
- Rigour, Reliability, and Validity (or Trustworthiness for qualitative research): How will you ensure the quality and credibility of your research? The methodology section of the PhD thesis outline should cover this.
- Results/Findings Chapters (Often Multiple): This is where you present the findings of your research, typically without extensive interpretation at this stage. Your PhD thesis outline should map out how these findings will be organised.
- Structure: Often organised by research question, theme, or hypothesis.
- Presentation: How will data be presented? (e.g., through tables, figures, graphs, direct quotes, case descriptions).
- Key Findings per Section: For each subsection, briefly note the main findings you anticipate presenting. This part of the PhD thesis outline connects directly to your data.
- Discussion Chapter: This is where you interpret your findings, relate them back to your research questions and the literature, and discuss their implications. The PhD thesis outline for the discussion is where your critical thinking shines.
- Summary of Key Findings (brief): Reiterate the most important results.
- Interpretation of Findings: What do your results mean in the context of your research questions?
- Relating to Literature: How do your findings confirm, contradict, or extend existing knowledge? Engage with the literature you reviewed earlier.
- Addressing Hypotheses/Research Questions: Explicitly state how your findings answer your initial questions or address your hypotheses.
- Theoretical Implications: How do your findings contribute to or challenge existing theories?
- Practical/Policy Implications (if applicable): What are the real-world applications or policy recommendations stemming from your research?
- Limitations of the Study: Acknowledge the limitations of your research in more detail here and suggest how they might have affected the findings.
- Novel Contributions: Re-emphasise the originality and contribution of your work. Crafting this part of the PhD thesis outline carefully is key.
- Conclusion Chapter: This chapter provides a final summary and draws everything to a close. Your PhD thesis outline for the conclusion should ensure a strong finish.
- Restatement of Aim and Objectives: Briefly remind the reader of what you set out to do.
- Summary of Main Findings and Arguments: Concisely summarise the key takeaways from your research.
- Overall Contribution: Reiterate the main contribution of your thesis.
- Implications (revisited concisely): Briefly touch upon key implications.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Suggest avenues for further investigation based on your findings and limitations.
- Concluding Remarks: A final, impactful statement. A clear PhD thesis outline helps shape these final thoughts.

- References/Bibliography: (A comprehensive list of all sources cited – your outline will implicitly build this list as you note key sources for each section).
- Appendices: (Supplementary materials like survey instruments, detailed data tables, interview transcripts (anonymised) – note in your PhD thesis outline what might go here).
This detailed breakdown forms the backbone of a truly robust PhD thesis outline, providing clarity and direction for the extensive PhD thesis writing process ahead.
Crafting Your PhD Thesis Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you understand the components, how do you actually go about creating your PhD thesis outline? Here’s a practical, step-by-step approach:
- Step 1: Brainstorming and Mind Mapping
- Start with your central research question(s) and objectives.
- Freely jot down all related ideas, concepts, arguments, theories, potential evidence, and key literature. Don’t filter yourself at this stage.
- Use tools like mind maps (software or pen and paper), sticky notes, or a large whiteboard to visually organize these initial thoughts. Group related ideas together. This initial brain dump is crucial for a comprehensive PhD thesis outline.
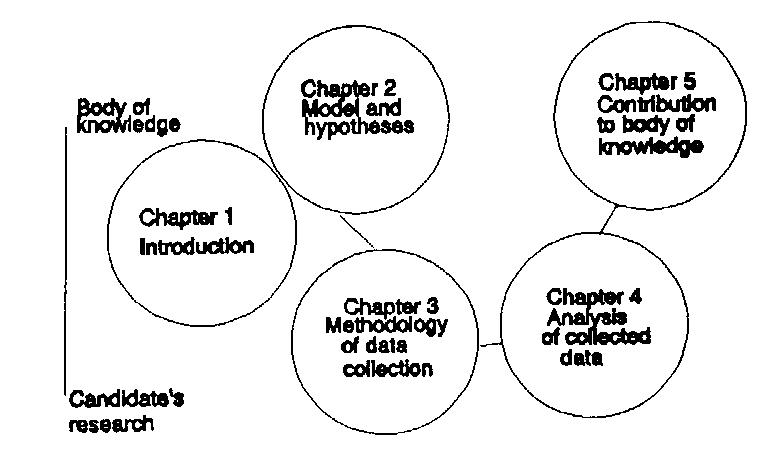
- Step 2: Structuring the Main Sections (The Macro-Outline)
- Based on the standard thesis structure (Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, etc., as discussed above), create the main chapter headings. This is the highest level of your PhD thesis outline.
- Consider if your research lends itself to multiple results or discussion chapters. For instance, if you have distinct phases of research or very different types of data, you might plan separate chapters.
- Step 3: Detailing Chapter by Chapter (The Micro-Outline)
- For each major chapter identified in Step 2, start breaking it down into logical sections and sub-sections.
- Use bullet points or a numbered/lettered hierarchy (e.g., 1.1, 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.2).
- For each subsection, write a brief descriptive phrase or sentence indicating its core content or argument.
- Example for an Introduction Chapter sub-section in your PhD thesis outline:
- 1.3 Problem Statement
- 1.3.1 Overview of current challenges in [specific area]
- 1.3.2 Identification of specific gap addressed by this research
- 1.3.3 Justification for the importance of addressing this gap
- 1.3 Problem Statement
- The goal here is to create enough detail in your PhD thesis outline so that you (or your supervisor) can understand the intended flow and content of each part of the thesis.
- Step 4: Adding Specifics – Arguments, Evidence, Key Sources
- Go back through your detailed chapter outlines and begin to flesh them out further.
- For each point or sub-section, note:
- The main argument you intend to make.
- Key pieces of evidence (e.g., specific data points you expect to find, pilot study results).
- Crucial authors or theories you will engage with.
- Specific methodologies or analytical tools to be used in relevant sections.
- This transforms your PhD thesis outline from a mere table of contents into a dynamic working document.
- Step 5: Reviewing, Refining, and Seeking Feedback
- Self-Review: Read through your entire PhD thesis outline.
- Does it flow logically from introduction to conclusion?
- Is there a clear “golden thread” – the central argument – running through it?
- Are all your research questions and objectives adequately addressed?
- Are there any gaps or redundancies?
- Is the scope realistic?
- Supervisor Feedback: This is critical. Share your detailed PhD thesis outline with your supervisor(s) for their input. They can provide invaluable guidance on structure, content, scope, and potential pitfalls. Be prepared to revise your PhD thesis outline based on their feedback. This iterative process is key to a strong final product.
- Self-Review: Read through your entire PhD thesis outline.
This systematic approach will help you build a comprehensive and useful PhD thesis outline.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Creating Your PhD Thesis Outline
Developing a strong PhD thesis outline is a skill. Being aware of common mistakes can help you avoid them:
- Being Too Vague: An outline with generic headings like “Data” or “Analysis” isn’t very helpful. The more detail, the better.
- Being Too Rigid: While detail is good, don’t be so attached to your initial PhD thesis outline that you’re unwilling to adapt it as your research evolves.
- Not Aligning the Outline with Research Questions: Every part of your PhD thesis outline should clearly contribute to answering your core research questions. If a section doesn’t, question its necessity.
- Skipping or Rushing the Preliminary Literature Review: A PhD thesis outline created without a solid understanding of the existing literature will likely be weak and misguided.
- Not Getting Supervisor Feedback Early and Often: Your supervisor’s experience is invaluable. Failing to consult them on your PhD thesis outline is a missed opportunity for crucial guidance.
- Underestimating the Time and Effort: Crafting a truly robust PhD thesis outline takes time and deep thought. Don’t treat it as a minor task to be rushed.
- Treating the PhD Thesis Outline as a One-Time Task: It should be revisited and refined throughout your PhD journey.

When and How to Seek Help
While crafting your PhD thesis outline is primarily your responsibility, seeking assistance is a sign of strength, not weakness.
- Supervisors: As mentioned repeatedly, your supervisor(s) are your first and most important resource. They can offer expert guidance on the structure and content of your PhD thesis outline.
- Peer Support Groups: Discussing your PhD thesis outline with fellow doctoral candidates can provide fresh perspectives and mutual support.
- University Writing Centers/Academic Skills Advisors: Many universities offer workshops or one-on-one consultations on thesis writing and structuring, which can be invaluable for refining your PhD thesis outline.
- Seeking External Assistance: If you are truly struggling with structuring your ideas, some students consider options for ” help with a PhD thesis outline “. At PhD Nurse Writer, we have reputable academic editors or consultants who can provide feedback on an existing draft of your PhD thesis outline, helping you to clarify its logic and coherence. Besides PhD thesis outline writing services, we can also help you with PhD thesis topic suggestion, thesis writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Our academic writing services also extend to essays, research papers, case studies, dissertations, term papers, assignments, proctored exams and ATI-TEAS tests.
Conclusion: The Value of a Robust PhD Thesis Outline
The journey to a PhD is a testament to dedication, intellectual curiosity, and perseverance. The PhD thesis outline is the unsung hero of this journey, providing the essential framework that supports and guides your monumental effort. Investing the time and intellectual energy to craft a robust, detailed, and adaptable PhD thesis outline is not just a preliminary step; it is a foundational act that profoundly influences the efficiency of your research, the clarity of your argument, and the overall quality of your final dissertation.
Embrace the process of creating your PhD thesis outline. See it as an opportunity to think deeply, to strategize effectively, and to lay a solid foundation for your scholarly contribution. A meticulously crafted PhD thesis outline will be your most trusted companion, guiding you through the complexities of doctoral research and helping you to articulate your unique voice and vision to the academic world. The strength of your final thesis often begins with the strength of your initial PhD thesis outline.