Table of Contents
The medical thesis is the culmination of years of rigorous study, dedicated research, and a burning desire to contribute to the field of medicine. It’s more than just a requirement for graduation; it’s an opportunity to delve deep into a specific area of interest, generate new knowledge, and potentially impact patient care. However, crafting an impactful medical thesis can seem daunting.
This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to navigate medical thesis writing successfully, ensuring your work leaves a lasting mark.
Laying the Foundation: Choosing the Right Medical Thesis Topic
The foundation of any successful medical thesis is a well-chosen research topic. A compelling topic should be:
- Relevant: Address a significant gap in current medical knowledge or a pressing clinical need. Consider exploring emerging trends or unresolved controversies within your chosen specialty.
- Feasible: Ensure the project is achievable within the available resources, timeframe, and your own skills. Consider sample size, data accessibility, and ethical considerations.
- Interesting: Select a topic that genuinely excites you. Passion will fuel your motivation and help you overcome challenges during the research and writing process.
- Specific and Focused: Avoid broad or vague topics. Narrow your focus to a well-defined research question that can be thoroughly investigated. For example, instead of “The impact of exercise on cardiovascular health,” consider “The effect of high-intensity interval training on endothelial function in patients with early-stage hypertension.”
Powerful Medical Thesis Topic Ideas
The following are powerful and compelling medical thesis topic ideas that can set you up for success. We’ll explore various domains within medicine, offering inspiration and strategies to help you narrow down your focus.
The Importance of a Strong Medical Thesis
A well-defined and researched medical thesis is a cornerstone of your academic journey. It demonstrates your ability to:
- Critically Analyze Medical Literature: Synthesizing existing research to identify gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Design and Conduct Research: Formulating a clear research question, choosing appropriate methodologies, and collecting relevant data.
- Interpret and Communicate Findings: Drawing meaningful conclusions from your data and presenting them in a clear and concise manner.
- Contribute to the Medical Field: Adding to the body of medical knowledge and potentially improving patient care.
Ultimately, a strong medical thesis not only fulfills a degree requirement but also lays the foundation for a future research career.
Navigating the Medical Landscape: Potential Topic Areas
To spark your creativity, consider exploring these diverse areas within medicine:
- Infectious Diseases:
- Investigating the impact of antibiotic resistance on treatment outcomes for specific infections.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of novel prevention strategies for emerging infectious diseases like Zika or Monkeypox.
- Exploring the role of microbiome dysbiosis in the development of chronic inflammatory conditions following infections.
- Cardiology:
- Evaluating the efficacy of telehealth interventions for managing patients with heart failure.
- Comparing the outcomes of different surgical approaches for treating atrial fibrillation.
- Examining the genetic predisposition to specific cardiovascular diseases in different ethnic populations.
- Oncology:
- Analyzing the impact of immunotherapy on long-term survival rates in specific cancer types.
- Investigating the role of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in early cancer detection and monitoring treatment response.
- Exploring the effectiveness of personalized medicine approaches based on individual tumor genomics.
- Neurology:
- Evaluating the efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, for managing chronic pain.
- Analyzing the impact of early intervention on the prognosis of patients with stroke.
- Investigating the role of neuroinflammation in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Public Health:
- Assessing the effectiveness of public health campaigns aimed at reducing rates of preventable diseases.
- Evaluating the impact of social determinants of health on access to healthcare and health outcomes.
- Investigating the ethical implications of using artificial intelligence in public health surveillance.
- Mental Health:
- Exploring the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in adolescents and young adults.
- Evaluating the efficacy of novel therapeutic approaches for treating anxiety and depression.
- Analyzing the impact of trauma-informed care on patient outcomes in various healthcare settings.
After generating a list of potential nursing thesis topics, it’s crucial to refine them into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) research questions. For example, instead of broadly exploring “the impact of immunotherapy on cancer,” you could refine it to “What is the impact of pembrolizumab on the overall survival rate of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer compared to traditional chemotherapy?”
Crafting a Powerful Research Question and Hypothesis
Once you have a general topic in mind, the next step is to formulate a clear and answerable research question. This question should guide your entire research process.
- Identify the problem: What is the specific issue you want to address?
- Define the population: Who are you studying?
- Determine the intervention or exposure: What are you investigating?
- Specify the outcome: What are you measuring?
- Consider the comparison group: What are you comparing your intervention or exposure to?
Based on your research question, you can then develop a hypothesis, which is a testable statement about the relationship between variables. A well-formulated hypothesis should be:
- Specific: Clearly define the expected relationship between variables.
- Measurable: Outline how the variables will be measured.
- Achievable: Feasible to test within the scope of your study.
- Relevant: Directly related to your research question.
- Time-bound: Specify the timeframe within which the relationship will be observed (if applicable).
Designing a Robust Medical Thesis Research Methodology
The methodology section is the backbone of your medical thesis. It describes the design, participants, procedures, and data analysis methods used in your research. A well-designed methodology ensures the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Study Design: Choose the most appropriate study design based on your research question. Options include:
- Randomized controlled trials (RCTs): Gold standard for evaluating interventions.
- Cohort studies: Observing a group of people over time to identify risk factors or outcomes.
- Case-control studies: Comparing individuals with a condition (cases) to those without (controls) to identify potential causes.
- Cross-sectional studies: Examining data at a single point in time.
- Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: Synthesizing evidence from multiple studies.
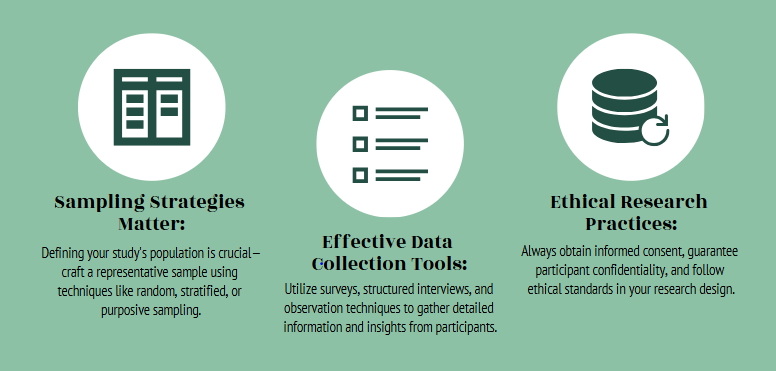
- Participants: Clearly define the inclusion and exclusion criteria for your study participants. Describe how you will recruit and enroll participants.
- Data Collection: Detail the methods you will use to collect data, including questionnaires, medical records, laboratory tests, and physical examinations. Ensure data collection procedures are standardized to minimize bias.
- Data Analysis: Specify the statistical methods you will use to analyze your data. Justify your choice of statistical tests and explain how you will handle missing data.
- Ethical Considerations: Obtain ethical approval from the relevant Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Ethics Committee. Ensure informed consent is obtained from all participants. Protect the privacy and confidentiality of participant data.
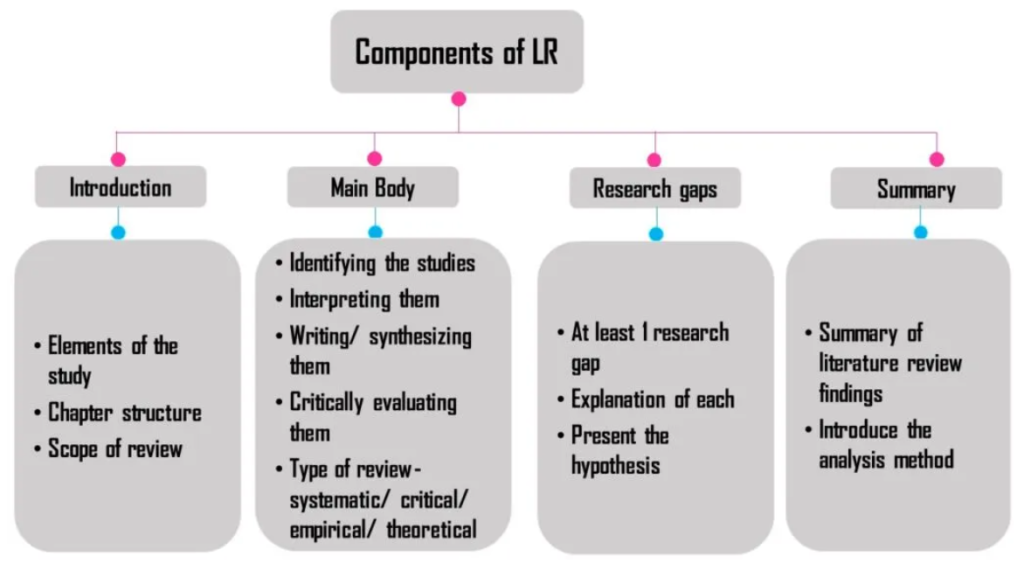
Conducting a Thorough Literature Review
The literature review is a critical component of your medical thesis. It demonstrates your understanding of the existing research on your topic and provides the context for your own study.
- Identify relevant sources: Use databases such as PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science to search for relevant articles, reviews, and guidelines.
- Critically evaluate the literature: Assess the quality and validity of the studies you review. Consider the study design, sample size, and statistical methods used.
- Synthesize the evidence: Summarize the key findings from the literature and identify gaps in current knowledge.
- Clearly state the rationale for your study: Explain how your research will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
- When considering the literature review, especially when facing time constraints, sometimes students look for help with medical thesis literature review components.
Check out this guide for more insights on how to write a robust nursing thesis literature review.
Writing a Compelling and Clear Medical Thesis
Writing a clear, concise, and well-organized medical thesis is essential for communicating your research findings effectively.
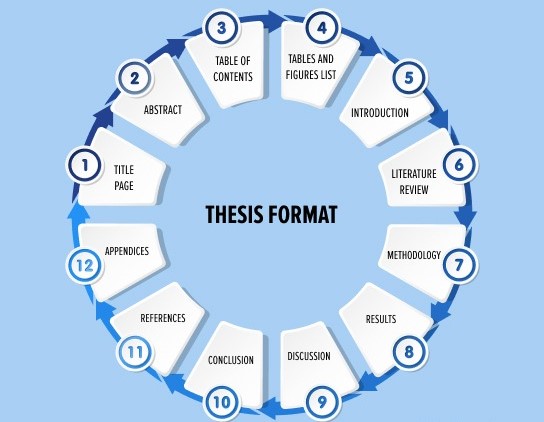
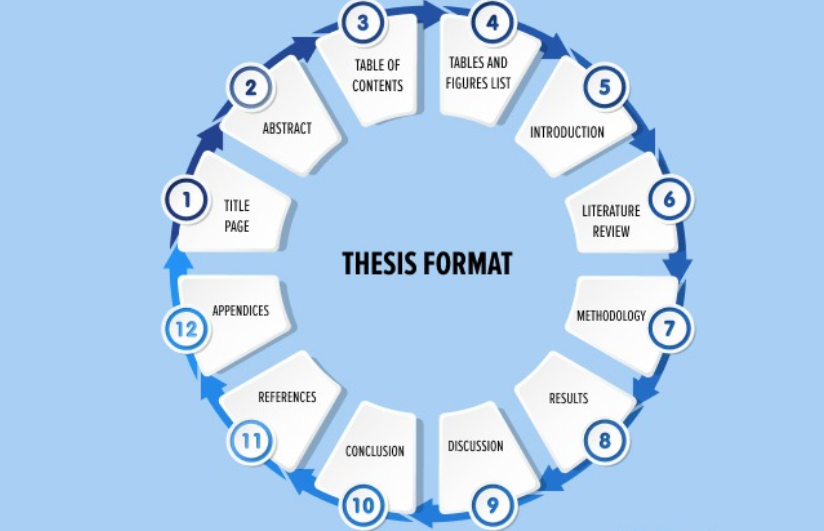
- Follow a standard structure: Most medical thesis follow a standard IMRAD format:
- Introduction: Provides background information on the topic, states the research question, and outlines the objectives of the study.
- Methods: Describes the study design, participants, data collection procedures, and data analysis methods.
- Results: Presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner, using tables and figures as appropriate.
- Discussion: Interprets the results, discusses their implications, and compares them to findings from previous studies.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the main findings of the study and outlines future research directions.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid jargon and technical terms that are not necessary. Use active voice whenever possible.
- Organize your thoughts logically: Use headings and subheadings to break up the text and make it easier to read.
- Proofread carefully: Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and typos. Ask a colleague or mentor to review your medical thesis before submitting it.
- Properly cite your sources: Use a consistent citation style (e.g., Vancouver, APA) to give credit to the authors of the works you have consulted.
Presenting Your Findings Effectively
Your medical thesis results deserve to be presented in a clear, concise, and visually appealing manner.
- Tables: Use tables to present numerical data in an organized format. Label each table clearly and provide a brief explanation of the data presented.
- Figures: Use figures (graphs, charts, images) to illustrate key findings. Label each figure clearly and provide a detailed caption.
- Text: Supplement your tables and figures with text that describes the main findings and highlights important trends.
Discussion: Interpreting Your Results and Their Implications
The discussion section is where you interpret your findings and discuss their implications for clinical practice, future research, and public health.
- Summarize your key findings: Briefly restate the main findings of your study.
- Interpret your results in light of previous research: Compare your findings to those of other studies. Explain any discrepancies or inconsistencies.
- Discuss the limitations of your study: Acknowledge any limitations of your study design, sample size, or data analysis methods.
- Suggest future research directions: Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Discuss the clinical implications of your findings: Explain how your findings could potentially improve patient care or public health.
Mastering Medical Thesis Writing: Key Considerations
Medical thesis writing requires a unique skill set. It’s not just about gathering information; it’s about critically analyzing it, synthesizing it, and presenting it in a way that is both informative and persuasive.
- Start early: Don’t wait until the last minute to start working on your medical thesis. The earlier you start, the more time you will have to conduct research, analyze data, and write your medical thesis.
- Seek guidance from your advisor: Your advisor is a valuable resource. Meet with them regularly to discuss your progress, ask questions, and get feedback.
- Stay organized: Keep track of your research materials, data, and writing drafts.
- Be persistent: Writing a medical thesis can be challenging. Don’t get discouraged if you encounter obstacles. Keep working at it and seek help when you need it.
- If stuck, the experts at PhD Nurse Writer can provide professional medical thesis writing services for proper guidance and support. We can help you with topic suggestion, thesis writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Apart from medical thesis, we also assist students in writing top-notch nursing research papers, essays, term papers and dissertations.
The Ethical Dimension of a Medical Thesis
A strong medical thesis is built on a foundation of ethical principles. Consider the following:
- Informed Consent: Ensure all participants are fully informed about the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits. Obtain their written consent to participate.
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality: Protect the privacy and confidentiality of participant data. Use de-identified data whenever possible.
- Authorship: Accurately credit all contributors to the research. Avoid plagiarism and ensure all sources are properly cited.
- Transparency and Disclosure: Disclose any potential conflicts of interest. Be transparent about the limitations of your study.
Common Pitfalls in Medical Thesis and How to Avoid Them
The journey of writing a medical thesis is fraught with potential pitfalls that can derail even the most promising projects. Recognizing these common errors and proactively implementing strategies to avoid them is crucial for a successful and rewarding experience.
Poorly Defined Research Question
One of the most frequent stumbles in a medical thesis lies in the formulation of a vague or overly broad research question. A weak question lacks focus, making it difficult to design an appropriate study, analyze the data effectively, and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Pitfall: A research question that is too general (e.g., “What is the effect of lifestyle on health?”) lacks the specificity required for a manageable research project.
- Avoidance: Employ the “FINER” criteria when formulating your question:
- Feasible: Can you realistically collect the necessary data with available resources and time?
- Interesting: Is the topic engaging and likely to contribute meaningfully to the field?
- Novel: Does the research address a gap in existing knowledge or offer a new perspective?
- Ethical: Can the study be conducted ethically, adhering to all relevant regulations and guidelines?
- Relevant: Is the research question important and applicable to clinical practice or public health?
- Example: Instead of the previous general question, a more focused question could be, “Does a 12-week structured exercise program improve HbA1c levels in adults with pre-diabetes compared to standard dietary advice?”
Inadequate Literature Review
Failing to conduct a comprehensive literature review is another common misstep. A thorough understanding of existing research is essential to avoid duplicating previous work, identify gaps in knowledge, and build a strong rationale for your study.
- Pitfall: Relying on a limited number of sources or focusing solely on recent publications without exploring foundational research.
- Avoidance: Dedicate sufficient time to exploring relevant databases (PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library), conference proceedings, and grey literature. Systematically analyze existing research, identify key concepts, and critically evaluate the strengths and limitations of previous studies. This will help you frame your research question within the context of existing knowledge and justify the need for your investigation.
Methodological Shortcomings
Flaws in study design, data collection, or data analysis can severely compromise the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Pitfalls:
- Using an inappropriate study design (e.g., cross-sectional study when a longitudinal design is required).
- Insufficient sample size, leading to low statistical power.
- Biased data collection methods (e.g., recall bias in retrospective studies).
- Incorrect statistical analyses.
- Avoidance: Carefully consider the research question and choose the most appropriate study design. Consult with a statistician early in the process to determine the required sample size and plan the statistical analyses. Develop clear and standardized data collection protocols to minimize bias. Ensure that all data are accurately entered and validated before analysis.
Ethical Considerations
Ignoring ethical considerations is a serious breach and can jeopardize the entire medical thesis.
- Pitfall: Failing to obtain informed consent from participants, not protecting patient confidentiality, or inappropriately manipulating data.
- Avoidance: Adhere strictly to ethical guidelines and regulations. Obtain approval from the institutional review board (IRB) or ethics committee before commencing the study. Clearly explain the purpose and procedures of the study to participants and obtain their informed consent. Ensure that all data are anonymized and stored securely to protect patient confidentiality.
Poor Writing and Presentation
Even well-conducted research can be undermined by poor writing and presentation.
- Pitfall: Using unclear language, lacking a logical structure, and failing to adhere to the required formatting guidelines.
- Avoidance: Write clearly and concisely, using precise language. Structure the medical thesis logically, following a standard format (introduction, methods, results, discussion, conclusion). Proofread carefully for grammatical errors and typos. Seek feedback from mentors and colleagues on clarity and organization. Adhere strictly to the formatting guidelines provided by your institution.
Time Management and Procrastination
Procrastination and poor time management can lead to a rushed and poorly executed medical thesis.
- Pitfall: Leaving tasks until the last minute, resulting in insufficient time for data collection, analysis, and writing.
- Avoidance: Develop a realistic timeline with achievable milestones. Break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks. Schedule regular meetings with your supervisor to discuss progress and address any challenges. Prioritize tasks and avoid distractions.
By proactively addressing these common pitfalls, medical students can increase their chances of producing high-quality research that contributes meaningfully to the medical field.
Beyond the Medical Thesis: Implications for Future Career
Completing a strong medical thesis can significantly benefit your future career. It demonstrates your research skills, critical thinking abilities, and commitment to advancing medical knowledge. It can also open doors to research opportunities, academic positions, and leadership roles in your chosen field.
For those considering advanced degrees in medicine, a robust thesis for medical school showcases a candidate’s ability to contribute meaningfully to the field.
Conclusion
Writing an impactful medical thesis is a challenging but rewarding endeavor. Following these guidelines can increase your chances of producing a high-quality medical thesis that makes a significant contribution to the field of medicine. Start early, seek guidance from your advisor, stay organized, and be persistent. And remember, whether you are tackling a nursing thesis, or focusing on a medical school thesis, the principles of rigorous research and clear communication remain paramount. Good luck with your medical thesis!