
Table of Contents
The nursing dissertation literature review is a crucial cornerstone of your research journey. It is more than a mere summary of existing knowledge; it serves as a bridge between your research question and the broader body of evidence in nursing. This critical analysis not only establishes the context for your study but also guides your methodology, informs your findings, and ultimately strengthens your conclusions.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to crafting a robust and insightful nursing dissertation literature review, encompassing essential steps, key considerations, and practical tips.
Steps to Crafting a Robust Nursing Dissertation Literature Review
1. Defining Your Focus: The Starting Point
Before embarking on the literature search, it is paramount to have a clear understanding of your research question. What gap in knowledge are you addressing? What specific area within nursing are you exploring? Having a well-defined focus helps you avoid getting lost in a sea of information and ensures that your nursing dissertation literature review remains relevant to your study.
Examples of Nursing Dissertation Literature Reviews with Defined Focus
- Focus: Impact of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Chronic Pain Management in Older Adults
This review will explore the current research on the efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) in reducing chronic pain and improving quality of life in older adults.
Key Questions:
- What types of MBIs have been studied in this population?
- What are the reported outcomes of these interventions?
- Are there specific populations of older adults who benefit most from MBIs?
- What are the potential mechanisms by which MBIs impact chronic pain?
- What are the limitations of existing research and areas for future investigation?
Potential Sources:
- Peer-reviewed journals (e.g., Journal of Pain, Pain Management Nursing, Geriatric Nursing)
- Clinical practice guidelines and evidence-based resources (e.g., NICE guidelines)
- Grey literature (e.g., reports from healthcare organizations, conference proceedings)
- Focus: Exploring the Lived Experiences of Nurses Caring for Patients with Advanced Dementia in Residential Care Settings
This review will examine the lived experiences of nurses working with patients with advanced dementia in residential care settings, exploring their challenges, coping mechanisms, and perceived needs.
Key Questions:
- What are the unique challenges faced by nurses caring for individuals with advanced dementia in residential care settings?
- How do nurses cope with the emotional, physical, and ethical demands of this work?
- What are the nurses’ perspectives on the resources and support they receive from their workplace?
- How do nurses perceive their own role in the care of these patients and their families?
- What are the implications of these experiences for improving nursing education, practice, and policy?
Potential Sources:
- Qualitative research studies (e.g., phenomenological, ethnographic, grounded theory)
- Journals focused on dementia care, palliative care, and gerontology
- Interviews and focus group discussions with nurses working in residential care settings
- Focus: Examining the Role of Technology-Assisted Learning in Promoting Nursing Students’ Critical Thinking Skills
This review will explore the effectiveness of technology-assisted learning (TAL) interventions in enhancing critical thinking skills among nursing students.
Key Questions:
- What types of TAL tools and interventions have been used to promote critical thinking in nursing education?
- What are the reported outcomes of these interventions in terms of students’ critical thinking skills?
- What are the potential mechanisms by which TAL promotes critical thinking?
- How do students’ perceptions and experiences with TAL impact their critical thinking development?
- What are the implications of these findings for the design and implementation of effective TAL interventions in nursing education?
Potential Sources:
- Educational research studies focusing on nursing education, technology integration, and critical thinking skills
- Journals related to nursing education, technology-enhanced learning, and educational psychology
- Reports and evaluations of TAL interventions in nursing programs
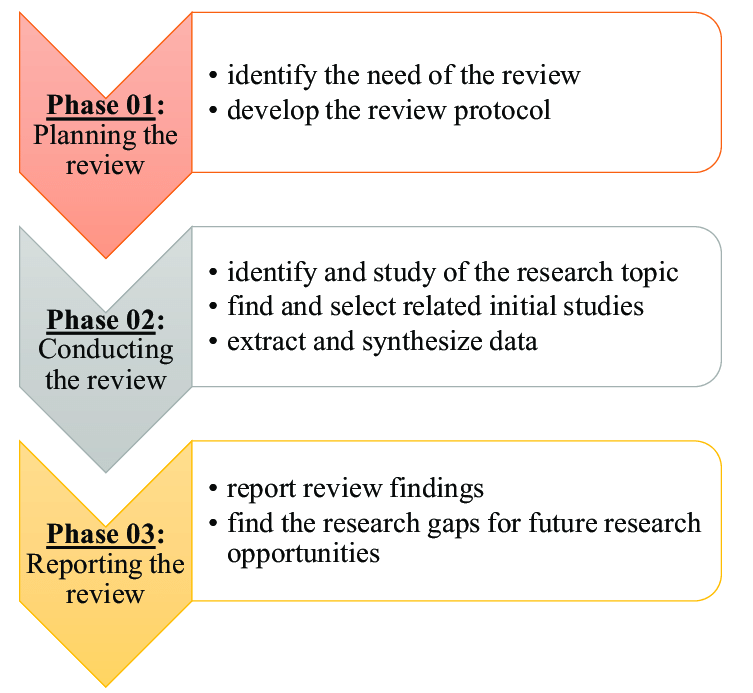
2. Comprehensive Search Strategies: Unearthing Relevant Literature
An effective literature review requires a systematic and comprehensive search strategy. This involves identifying the appropriate databases, keywords, and search filters.
- Databases: Familiarize yourself with databases specifically relevant to nursing research, such as CINAHL, PubMed, PhD Nurse Writer and Medline. Additionally, explore databases catering to your specific area of interest, like PsycINFO for mental health or ERIC for education.
- Keywords: Craft a list of relevant keywords encompassing your research question, key concepts, and related terms. Use a combination of broad and specific keywords, and explore synonyms and related terms to expand your search.
- Search Filters: Employ filters to narrow down your search results. Consider factors such as publication date, language, study type (e.g., randomized controlled trials, qualitative studies), and population group.
3. Critical Evaluation: Sifting through the Evidence
Once you have compiled a list of potential sources, it’s crucial to critically evaluate their quality and relevance. This involves assessing:
- Relevance: Does the source directly address your research question? Does it contribute to understanding the gap in knowledge you are aiming to fill?
- Credibility: Is the source authored by experts in the field? Is it published in a reputable journal or by a trusted organization?
- Methodology: Is the research methodology sound and appropriate for the research question? Are the findings supported by evidence and data?
- Bias: Does the source exhibit any biases or potential conflicts of interest that might influence its findings?
4. Organizing Your Findings: Building a Structure
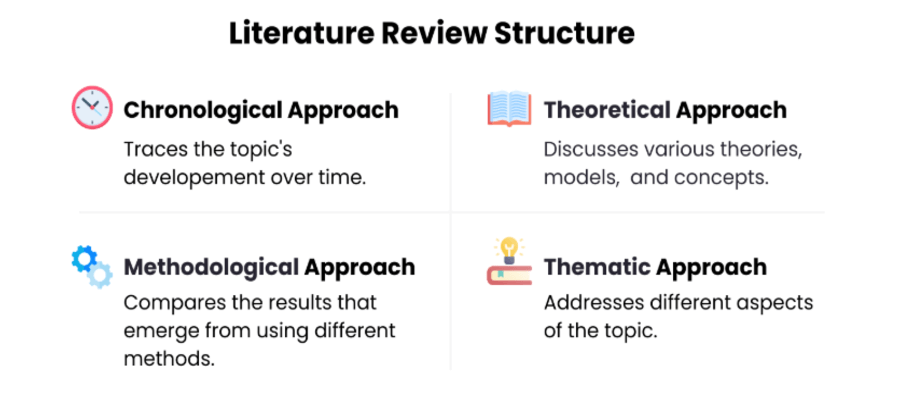
A well-structured nursing dissertation literature review enhances readability and clarity. Consider these common organizational approaches:
- Thematic: Organize the review by themes or subtopics related to your research question. This approach allows you to explore various aspects of the existing literature in a structured manner.
- Chronological: Present the literature in chronological order, highlighting the evolution of research and knowledge within your field.
- Problem-Solution: Group the literature based on problems or challenges within your research area and present relevant solutions or interventions.
5. Engaging with the Literature: Beyond Summary
Your nursing dissertation literature review should go beyond simply summarizing existing studies. You need to critically analyze, synthesize, and interpret the information, drawing connections and identifying gaps in the literature.
- Analysis: Compare and contrast different findings, identify conflicting results, and discuss potential limitations of existing research.
- Synthesis: Identify common themes and patterns emerging from the literature, highlighting key insights and emerging trends.
- Gap Identification: Critically analyze the literature to identify gaps in knowledge, unanswered questions, and areas requiring further exploration. These gaps will provide justification for your research and contribute to the development of your research question.
6. Writing a Clear and Concise Narrative
A compelling nursing dissertation literature review is characterized by clear, concise, and well-structured writing.
- Clarity: Use precise language, avoid jargon, and define key terms. Ensure that the flow of your writing is logical and easy to follow.
- Conciseness: Focus on the essential information, avoid unnecessary details, and prioritize relevant insights.
- Structure: Employ headings and subheadings to organize the review and guide the reader through the key themes and arguments.
7. Connecting to Your Research: Bridging the Gap
The most impactful nursing dissertation literature review clearly demonstrates the relevance of your research within the broader context of existing knowledge.
- Relate findings: Connect the findings of your literature review to your research question, highlighting how your study will contribute to the existing body of evidence.
- Highlight gaps: Emphasize the specific gaps in knowledge that your study aims to address. This demonstrates the unique contribution of your research and its potential impact on the field.
- Justify methodology: Explain how the literature review informed your choice of research methods and design. This demonstrates that your study is grounded in existing evidence and built upon previous research.
8. Avoiding Common Pitfalls: Ensuring Quality
To ensure a high-quality nursing dissertation literature review, avoid these common pitfalls:
- Over-reliance on secondary sources: While secondary sources can offer a broader overview of the field, they should not replace primary research articles. Prioritize primary sources for your analysis.
- Ignoring opposing views: Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints or conflicting findings within the literature. This demonstrates critical thinking and a balanced approach to the topic.
- Unclear connections: Ensure that each paragraph and section of your review seamlessly flows into the next, demonstrating clear connections between the literature and your research question.
9. Staying Updated: Embracing Continuous Learning
The field of nursing is constantly evolving, with new research emerging frequently. To ensure your nursing dissertation literature review remains relevant, engage in continuous learning.
- Monitor key journals: Subscribe to or regularly check major nursing journals for the latest research in your field.
- Attend conferences: Participate in conferences and workshops to stay abreast of current trends and emerging topics.
- Network with experts: Engage with researchers and practitioners in your field, attending seminars, webinars, and networking events.
10. The Importance of Ethical Practices: Respecting Authors and Ideas
As you engage with the existing literature, it is crucial to respect the intellectual property and contributions of other researchers.
- Proper citations: Use consistent and accurate citation methods, such as APA style, to give credit to the original authors and prevent plagiarism.
- Quoting responsibly: Use quotes sparingly and only when necessary to emphasize a specific point or provide a unique perspective.
- Summarize effectively: Accurately summarize the key findings and arguments of each source, avoiding misrepresentation or distortion of the original work.

How to Avoid Mistakes in Your Nursing Dissertation Literature Review
A strong nursing dissertation literature review is crucial for a successful dissertation. It provides context, identifies gaps in knowledge, and strengthens your argument. However, several common mistakes can weaken your review, making it difficult for your readers to understand the significance of your research. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
1. Lack of Focus and Direction: A nursing dissertation literature review must be tightly focused on your research question. Avoid including irrelevant studies or information that doesn’t directly contribute to your argument. Instead, select and analyze literature that directly relates to your chosen topic.
2. Insufficient Critical Analysis: Simply summarizing existing research is not enough. Your nursing dissertation literature review should critically evaluate the literature, highlighting strengths, limitations, and potential biases. Analyze the findings, compare and contrast different studies, and identify areas for further exploration.
3. Inadequate Synthesis: A nursing dissertation literature review should not be a list of separate studies. Instead, synthesize the information, drawing connections between different studies and highlighting emerging themes and patterns.
4. Overreliance on Secondary Sources: While secondary sources can be helpful, prioritize primary research articles. A nursing dissertation literature review should be based on original research findings, not just summaries of other reviews.
5. Neglecting Recent Literature: The nursing dissertation literature review should include the most current research findings. Make sure to include recent publications to demonstrate your knowledge of the latest advancements and debates in your field.
6. Poor Organization and Structure: A well-structured nursing dissertation literaturereview is essential for clarity and coherence. Organize your review logically, using headings and subheadings to guide the reader through the information.
7. Lack of Clarity and Conciseness: Avoid using jargon or overly complex language. Write in a clear and concise style, ensuring your readers can easily understand your arguments.
8. Inadequate References and Citation: Accurate and consistent citations are critical. Ensure all sources are properly acknowledged and formatted according to the required style guide.
Carefully avoiding these common mistakes will enable you to write a strong and persuasive nursing dissertation literature review that effectively supports your research and demonstrates your understanding of the current state of knowledge in your chosen field.
Example: Nursing Dissertation Literature Review: Impact of Mindfulness on Pain Management in Cancer Patients
Let’s illustrate the practical application of these guidelines with an example. Imagine a nursing dissertation focusing on the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on pain management in cancer patients. The nursing dissertation literature review would:
- Define the focus: The review would focus on the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for reducing pain and improving quality of life in cancer patients.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Relevant databases would include CINAHL, PubMed, and PsycINFO. Keywords would include “mindfulness,” “cancer pain,” “pain management,” “quality of life,” and “intervention.”
- Critically evaluate sources: The review would focus on studies with robust methodologies, such as randomized controlled trials or mixed methods designs, that have examined the efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions in cancer pain management.
- Organize the findings: The review could be organized thematically, exploring the following areas: (a) effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions on pain intensity, (b) impact on pain-related distress and anxiety, (c) influence on sleep quality and overall quality of life, and (d) potential mechanisms of action.
- Engage with the literature: The review would go beyond summarizing findings and analyze the consistency of evidence, identify potential limitations, and highlight gaps in the literature. For instance, the review might address the need for further research on the long-term effects of mindfulness interventions on pain management, the effectiveness of different mindfulness techniques, and the potential for personalized interventions tailored to individual patient needs.
- Connect to research: The nursing dissertation literature review would then clearly connect to the research question, demonstrating how the study will contribute to existing knowledge by examining the impact of a specific mindfulness-based intervention on pain management in a specific population of cancer patients.
- Avoid common pitfalls: The review would ensure accurate citations, acknowledge opposing viewpoints, and maintain a clear and logical flow of ideas.
- Stay updated: The researcher would continuously monitor relevant journals and attend conferences to ensure the review remains current and relevant.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Dissertation Literature Review
- What is the purpose of a nursing dissertation literature review?
The purpose of a nursing dissertation literature review is to provide a comprehensive overview of existing research on your chosen topic. It helps you identify gaps in knowledge, establish the significance of your research question, and justify your chosen methodology.
- How do I choose the right sources for my nursing dissertation literature review?
Start with reputable sources like peer-reviewed journals, books, and grey literature. Ensure the sources are relevant to your research question and published within the last 5-10 years.
- What are the different types of literature reviews in a nursing dissertation?
There are several types of nursing dissertation literature review, including narrative, systematic, and scoping reviews. The type you choose depends on your research question and objectives.
- What are the key components of a well-structured nursing dissertation literature review?
A well-structured nursing dissertation literature review includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The body should be organized thematically and present a critical analysis of the literature, highlighting key findings, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps.
- How do I critically evaluate the sources for my nursing dissertation literature review?
Critically evaluate sources based on their methodology, findings, limitations, and relevance to your research question. Look for methodological rigor, appropriate sampling, and clear conclusions.
- How do I synthesize the findings of different studies in my nursing dissertation literature review?
Use tables, charts, or narrative summaries to synthesize findings. Compare and contrast different studies, highlight common themes, and identify areas of agreement and disagreement.
- How do I identify gaps in the literature for my nursing dissertation literature review?
By critically evaluating the existing research, you can identify gaps in knowledge, such as areas where further research is needed, under-explored topics, or conflicting findings.
- How long should my nursing dissertation literature review be?
The length of your nursing dissertation literature review depends on the scope and complexity of your research. It is typically a significant section of the dissertation, usually 20-30 pages.
- What are some common mistakes to avoid in my nursing dissertation literature review?
Avoid simply summarizing the literature without critical analysis. Ensure you have a clear research question, avoid bias in your interpretation, and provide a clear link between the literature review and your own research.
- Where can I find help with my nursing dissertation literature review?
Your university library resources, research advisors, and online resources can provide guidance and support throughout the process of writing your nursing dissertation literature review.
A Foundation for Success
A well-written nursing dissertation literature review is a cornerstone of a successful dissertation. By meticulously following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can craft a robust and impactful literature review that informs your research question, justifies your methodology, and ultimately contributes to the advancement of nursing knowledge.
Remember, the nursing dissertation literature review is not simply an exercise in summarizing existing knowledge; it is a crucial opportunity to critically analyze, synthesize, and interpret the evidence, laying the foundation for your own original contribution to the field.
Get Customized Nursing Dissertation Writing Service
At PhD Nurse Writer, we offer professional nursing dissertation writing help for Master’s and PhD. We can assist you with crafting all dissertation sections including literature review, methodology and discussion. Our service covers dissertation writing, proofreading and editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Besides dissertations, we can also help you to write original nursing essays, case studies and research papers.





