Table of Contents
The undergraduate nursing dissertation is often the most significant academic project of a nursing student’s degree. It’s a culmination of all the learning, critical thinking, and practical experience accumulated during your studies. However, the prospect of undertaking such a large and demanding project can feel daunting. This article breaks down the process, providing a comprehensive guide to writing a successful undergraduate nursing dissertation.
The Importance of the Undergraduate Nursing Dissertation
Before we dive into the how-to, it’s crucial to appreciate why this dissertation holds such weight. It’s not simply a long essay; it’s an opportunity to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking and analytical skills: You’ll need to evaluate existing research, synthesize information, and form your own well-supported conclusions.
- Showcase your research abilities: This involves formulating a research question, selecting appropriate methodologies, and analyzing your findings.
- Contribute to the body of nursing knowledge: Even at the undergraduate level, your research can contribute valuable insights to the field.
- Develop your academic writing skills: Successfully completing an undergraduate nursing dissertation refines your ability to communicate complex ideas clearly and concisely.
- Prepare you for future research or advanced studies: If you’re considering a master’s degree or further research, the dissertation provides invaluable experience.
Planning is Paramount: Setting the Foundation for Success
The key to a good undergraduate nursing dissertation lies in the planning phase. Jumping straight into writing is a recipe for disaster. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Choosing a Topic: This is perhaps the most crucial step. Your topic should be:
- Relevant: It should address a significant issue in nursing practice or theory.
- Manageable: It should be scoped appropriately for the time and resources available at an undergraduate level.
- Interesting: You’ll be spending a lot of time on this project, so choose something you’re genuinely passionate about.
- Supported by Literature: Ensure there’s sufficient existing research to draw upon.
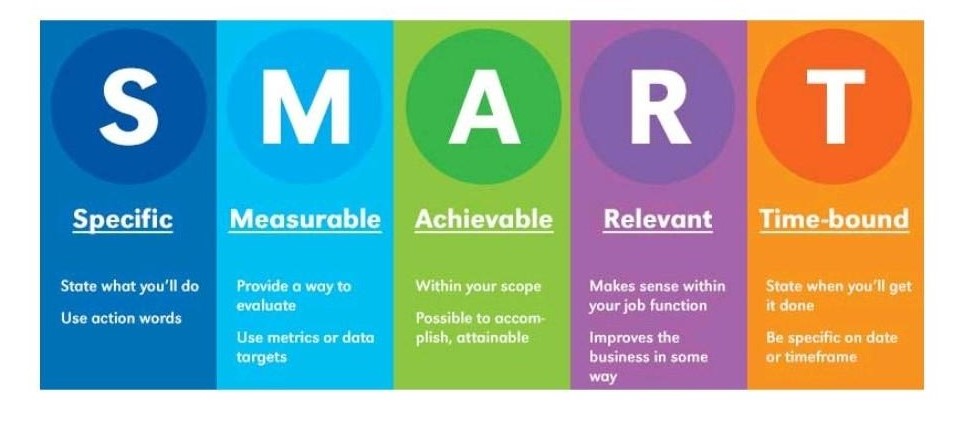
- Developing a Research Question: Once you have a topic, formulate a clear and focused research question. This question will guide your entire project. It should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Examples: Instead of “What are the effects of stress on nurses?” try “What is the impact of shift work on the self-reported stress levels of registered nurses in acute care settings?”
- Conducting a Literature Review: This is a deep dive into existing research on your topic. It allows you to:
- Identify gaps in knowledge: What areas haven’t been explored sufficiently?
- Understand the theoretical framework: Which theories are relevant to your topic?
- Justify your research: Why is your research necessary?
- Develop your argument: How does your research build upon the work of others?
- Use reputable sources: Utilize peer-reviewed journals, academic books, and reports. Websites should be critically evaluated for credibility.
- Choosing Your Research Methodology: This depends on your research question and the type of information you seek. Common approaches include:
- Quantitative: Collecting numerical data that can be statistically analyzed (e.g., surveys, experiments).
- Qualitative: Collecting descriptive data to understand experiences, perspectives, and meanings (e.g., interviews, focus groups).
- Mixed Methods: Combining both quantitative and qualitative approaches.
- Consider limitations: Think realistically about what you can achieve within your timeframe and resources when selecting the methodology.
- Creating a Timeline: Divide your project into manageable stages with specific deadlines. This helps you stay on track and avoid last-minute stress.
Writing Your Nursing Dissertation: A Structured Approach
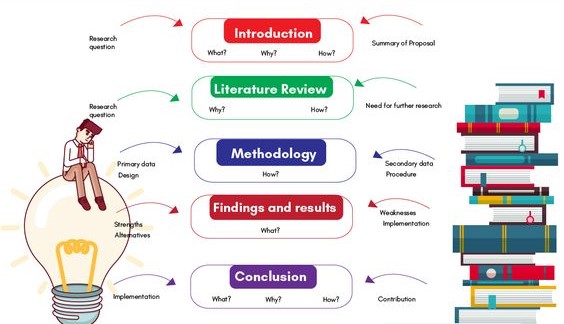
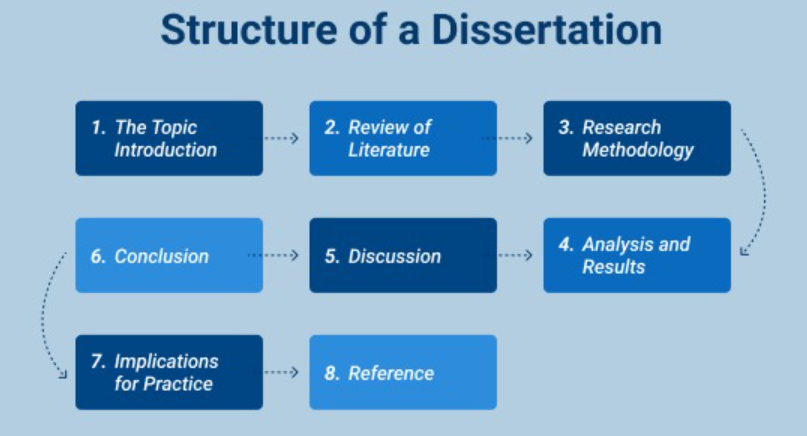
Once you’ve thoroughly planned, it’s time to start writing. The structure of an undergraduate nursing dissertation typically follows a specific format:
- Abstract: A concise summary of your entire dissertation (usually around 250-300 words). It includes your research question, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
- Introduction: This section introduces your topic, states your research question, outlines the significance of your study, and briefly previews the structure of your dissertation.
- Literature Review: This is a detailed analysis of existing research related to your topic. It should identify gaps in knowledge, justify your study, and provide the theoretical background.
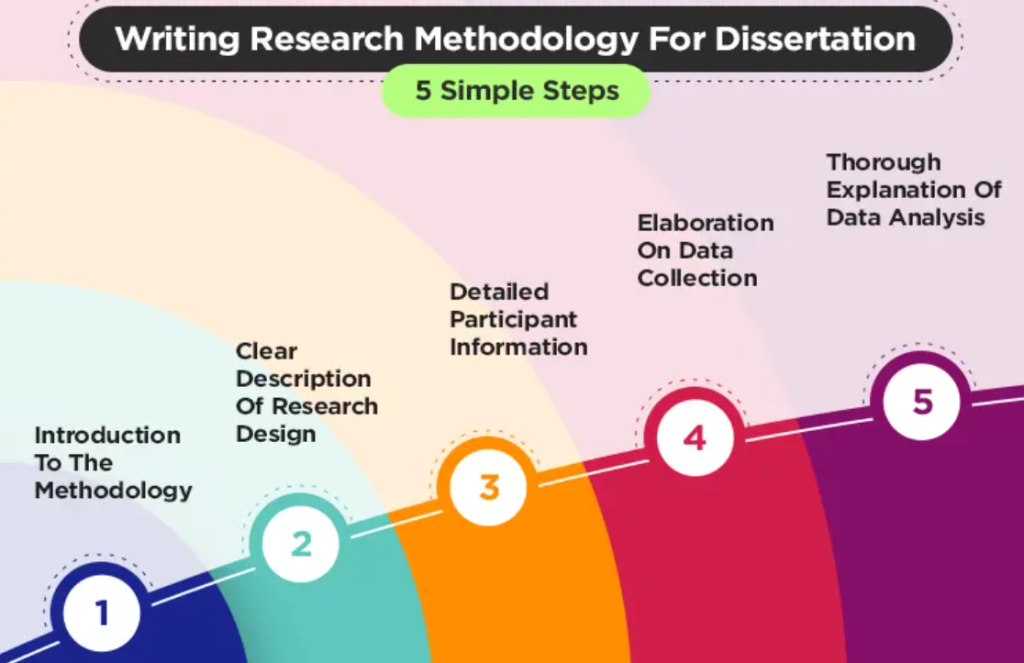
- Methodology: This section explains how you conducted your research. It should detail:
- Your research design (quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods).
- Your sample (participants and how they were selected).
- Data collection methods (surveys, interviews, observations).
- Data analysis techniques.
- Ethical considerations (e.g., informed consent, anonymity).
- Results: Present your findings clearly and objectively.
- Quantitative Results: Use tables, charts, and graphs to present numerical data.
- Qualitative Results: Use themes and illustrative quotes from interviews or other qualitative data sources.
- Avoid drawing conclusions in this section; that comes in the discussion.
- Discussion: This is where you interpret your findings, discuss their implications, and answer your research question.
- Relate findings to the literature: Do your findings support or contradict existing research?
- Discuss limitations: Be honest about any limitations of your study.
- Suggest further research: What areas need further investigation?
- Conclusion: A summary of your key findings and their implications.
- Reiterate the significance: Why is your research important?
- Offer a final message: What is the take-home message of your dissertation?
- References: A complete list of all the sources you cited in your dissertation. Use a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, Harvard).
- Appendices: Include any supplementary materials, such as interview transcripts or questionnaires.
Tips for Writing an Effective Nursing Dissertation
Here are some practical tips to help you navigate the writing process:
- Maintain a clear and concise writing style: Avoid jargon and use simple, straightforward language.
- Use an academic tone: Avoid informal language, slang, or personal opinions.
- Be consistent: Ensure consistency in your writing style, citation style, and formatting throughout the dissertation.
- Proofread carefully: Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Consider asking a friend or colleague to proofread your work as well.
- Seek feedback: Ask your supervisor for feedback at different stages of the writing process. This can help you identify areas for improvement.
- Don’t procrastinate: Start early and work consistently. This will reduce stress and allow you ample time for revision.
- Stay organized: Keep your research materials organized and labeled. Use software tools to manage your references and notes.
- Take breaks: Regular breaks can help you stay focused and prevent burnout.
- Remember why you started: Focus on the importance of your project and the potential impact it can have.
Navigating Challenges in the Nursing Dissertation Writing Process
The journey of an undergraduate nursing student culminates, for many, in the daunting task of completing an undergraduate nursing dissertation. This significant piece of academic work requires a combination of research skills, critical thinking, and effective writing, and it often presents students with a unique set of challenges. Understanding these hurdles and developing strategies to overcome them is crucial for success. The following are some of the common pitfalls, with practical advice to help you navigate this demanding process.
Choosing a Manageable and Relevant Topic
- The Challenge: Many students struggle to identify a focused and feasible research topic for their undergraduate nursing dissertation. They may choose a topic that’s too broad, too complex, or not relevant to current nursing practice. This leads to frustration, difficulty in research, and an inability to reach a meaningful conclusion.
- How to Avoid It:
- Start Early: Begin brainstorming ideas well in advance. Talk to your lecturers, supervisors, and even practicing nurses about areas of interest or current issues in the field.
- Be Specific: Instead of tackling broad topics, break them down into smaller, more manageable questions. For instance, rather than “The Role of Technology in Healthcare,” consider “The Impact of Telemedicine on Patient Satisfaction in Rural Nursing Practice.”
- Assess Feasibility: Consider the resources available to you. Do you have access to the necessary research participants, data, or equipment? Can the research be realistically completed within the given time frame?
- Relevance is Key: Ensure the topic aligns with your interests and offers a valuable contribution to nursing knowledge or practice.
Conducting Effective Literature Reviews
- The Challenge: A comprehensive literature review is crucial to understanding the context of your research and identifying gaps in current knowledge. Students often find themselves overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information or struggle to critically analyze the sources.
- How to Avoid It:
- Develop a Critical Eye: Don’t just summarize the articles; analyze them. Look for strengths, weaknesses, biases, and limitations in the research. Identify how they contribute to your topic.
- Organize Your Findings: Create a system (e.g., tables, mind maps) to organize the information you gather, which will help in the writing process.
Methodological Rigor
- The Challenge: Choosing the right research methodology and adhering to its principles can be another hurdle. Students may struggle with issues of validity, reliability, ethical considerations, and data analysis. This can weaken the credibility of the undergraduate nursing dissertation.
- How to Avoid It:
- Seek Guidance: Consult with your supervisor early and frequently. Discuss the appropriateness of your chosen method and address any potential ethical issues.
- Be Clear and Concise: Clearly explain your methodological choices and justify why they are suitable for your research question.
- Adhere to Ethical Guidelines: Ensure you understand and adhere to the principles of informed consent, confidentiality, and data protection.
Writing and Time Management
- The Challenge: Many students struggle with the actual writing process, often facing procrastination, writer’s block, and difficulty structuring their ideas effectively. Poor time management can make the task feel insurmountable.
- How to Avoid It:
- Break it Down: Divide the dissertation into smaller, manageable sections (introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion). This makes the task feel less overwhelming.
- Create a Schedule: Set realistic deadlines for each section. Stick to your schedule and avoid procrastination.
- Seek Feedback: Share drafts with peers or your supervisor and be receptive to feedback. This can significantly improve the quality of your undergraduate nursing dissertation.
- Proofread Carefully: Edit and proofread your dissertation meticulously before submission. Typos, grammatical errors, and inconsistencies detract from the overall impression of your work.
Proactively addressing the common challenges outlined above and utilizing effective strategies will enable you to confidently navigate the process and produce a high-quality undergraduate nursing dissertation that showcases your knowledge, skills, and dedication to the profession. With careful planning, effective research, and diligent writing, students can achieve success and contribute meaningfully to the field of nursing.
Sometimes, students feel overwhelmed and may search for terms like “nursing dissertation for undergraduate”, “nursing dissertation writing”, or “nursing dissertation writer.” While seeking help is acceptable, be cautious when engaging services promising to “write my nursing dissertation” entirely. Ensure you maintain academic integrity, and any external help should be for guidance and support only. Your work must be original.
FAQs about Undergraduate Nursing Dissertation
What is the purpose of an undergraduate nursing dissertation?
The undergraduate nursing dissertation serves multiple crucial functions. Primarily, it demonstrates your ability to conduct independent research, analyze information critically, and synthesize knowledge in a focused area of nursing. It’s an opportunity to delve deeply into a topic that genuinely interests you, showcasing your grasp of research methodology and ethical considerations relevant to nursing practice. Furthermore, it helps you develop advanced academic writing skills and build a solid foundation for future postgraduate studies, should you choose to pursue them. Essentially, the undergraduate nursing dissertation allows you to apply everything you’ve learned throughout your degree in a practical and meaningful way.
How do I choose a topic for my undergraduate nursing dissertation?
Selecting a topic is often the first hurdle. It’s important to choose something that genuinely sparks your interest, as you’ll be spending a considerable amount of time researching and writing about it. Consider areas of nursing practice where you feel there’s room for improvement or a particular patient population that fascinates you. Talk to your lecturers or potential supervisors; their guidance can help you narrow down your focus and ensure that your chosen topic is manageable within the scope of an undergraduate project.
Remember, a good topic is researchable, relevant, and allows you to contribute meaningfully to the nursing field. Avoid topics that are too broad or lack sufficient literature to support your arguments. A well-defined topic forms the bedrock of a successful undergraduate nursing dissertation.
What kind of research methods can I use?
The research methods you employ depend largely on your chosen topic and the available resources. Quantitative methods, involving numerical data collection and analysis (like questionnaires or surveys), are common. Qualitative methods, focusing on exploring experiences and perspectives (through interviews or focus groups), are also frequently used. Some students opt for a literature review, which involves critically evaluating existing research on the topic. Your university may have specific preferences or guidelines. It’s critical to consult with your supervisor to ensure your chosen methods are appropriate and achievable. The key is to select methods that will effectively answer your research question for your undergraduate nursing dissertation.
How much time should I dedicate to my undergraduate nursing dissertation?
Effective time management is crucial. Start your research early, even before the official commencement date, if possible. Break the project down into manageable tasks, setting realistic deadlines for each stage, including proposal development, literature review, data collection (if applicable), analysis, writing, and editing. Dedicate specific hours each week to working on your dissertation, treating it like a regular commitment. This consistency is key to avoiding the last-minute rush and ensuring you produce high-quality work. Remember that writing an undergraduate nursing dissertation is a marathon, not a sprint.
What support is available to me?
Your university should offer substantial support for completing your dissertation. Your allocated supervisor is a key resource, providing guidance on your topic, research methods, and overall structure. Library services often provide training and resources for effective literature searching. Writing centers can help refine your writing skills and ensure your work meets academic standards. Don’t hesitate to utilize these resources. Seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
How is my undergraduate nursing dissertation graded?
Grading criteria vary slightly between institutions, but generally consider several key aspects. These often include the quality of your research, the rigor of your analysis, the clarity of your writing, the coherence of your arguments, and the appropriate use of academic conventions. A clear understanding of the grading rubric is crucial to maximizing your chances of success with your undergraduate nursing dissertation.

Final Thoughts
Writing an undergraduate nursing dissertation is a challenging but rewarding experience. It’s an opportunity to deepen your understanding of a particular area of nursing and make a valuable contribution to the field. By following a structured approach, planning thoroughly, and seeking help when needed, you can successfully complete this significant project. Your undergraduate nursing dissertation is a testament to your dedication, hard work, and critical thinking skills.
The skills developed throughout the writing of your undergraduate nursing dissertation will benefit you long into your nursing career. Remember, your undergraduate nursing dissertation is a stepping stone to professional growth. Don’t underestimate the power of thedissertation in showcasing your capabilities. It is a testament to your understanding of the complex field of nursing, and completing an undergraduate nursing dissertation is a major achievement in your academic career.
If you need professional help with writing an undergraduate nursing dissertation, do not hesitate to engage PhD Nurse Writer. We have highly experienced researchers and writers to deliver an authentic and top notch undergraduate dissertation at your convenience. We also help students with writing research papers, essays and case studies.