Table of Contents
The nursing care plan is the bedrock of quality patient care. It’s a dynamic, patient-centered document that outlines a roadmap for achieving the best possible health outcomes. It’s more than just a checklist; it’s a critical thinking exercise that reflects the nurse’s assessment, understanding, and planning for an individual patient’s unique needs. A well-written nursing care plan ensures consistency, promotes collaboration among healthcare professionals, and ultimately contributes to a higher standard of care. Whether you’re a seasoned nurse or a student, mastering the art of creating stellar nursing care plans is paramount.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to crafting effective plans that truly make a difference.
Understanding the Essence of a Nursing Care Plan
Before delving into the ‘how-to’, it’s important to understand what makes a good nursing care plan so vital. Nursing care plans serve several crucial purposes:
- Provides a structured approach to care: It moves beyond simply responding to immediate issues to actively planning for the patient’s holistic needs.
- Promotes individualized care: It ensures care is tailored to the patient’s specific condition, preferences, and goals.
- Facilitates communication: It creates a clear and consistent roadmap for all healthcare team members involved in the patient’s care.
- Ensures continuity of care: It provides a reference point for nurses across different shifts and days, avoiding fragmentation of care.
- Serves as a legal document: It provides a record of the nursing process, which is important for legal and professional accountability.
- Supports evaluation of care: It offers a baseline to measure the effectiveness of nursing interventions and make necessary adjustments.
A nursing care plan, in essence, is the bridge between nursing assessment and nursing intervention. It transforms the nurse’s astute observations into a strategic action plan designed for the patient’s well-being.
The Key Elements of a Stellar Nursing Care Plan
Crafting an effective nursing care plan involves several key components that work together to create a comprehensive patient-centered roadmap. Here are the core elements you should always include:
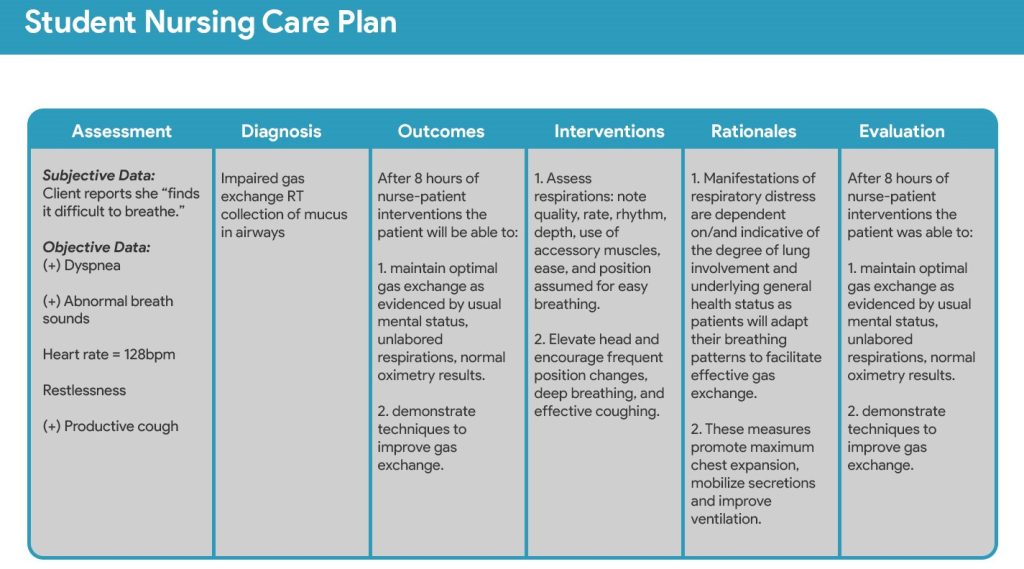
- Assessment: This is the foundation of the entire plan. It involves a thorough collection of data about the patient’s physical, psychological, social, and spiritual needs. This includes:
- Patient history: Past medical conditions, surgeries, and allergies.
- Current health status: Vital signs, physical assessment findings, and mental status.
- Patient’s perspective: What concerns the patient, their goals, and preferences for care.
- Family history: Relevant information that might impact the patient’s current health or treatment.
- Psychosocial needs: Assessing their support system, emotional state, and cultural background.
- Nursing Diagnoses: Based on the assessment data, the nurse identifies specific problems or potential risks the patient is experiencing. These are formulated as nursing diagnoses, which are distinct from medical diagnoses. Here’s how to approach it:
- Use standardized language: Refer to resources like NANDA-I to correctly identify nursing diagnoses.
- Prioritize diagnoses: Focus on the most urgent needs and safety concerns first.
- Formulate diagnostic statements correctly: Use the PES (Problem, Etiology, Signs and Symptoms) format for clarity.
- Goals and Outcomes: These are the desired changes in the patient’s condition that you want to achieve through nursing interventions. Goals should be:
- Patient-centered: Stated from the patient’s perspective, not the nurse’s.
- Specific: Clearly define the desired outcome.
- Measurable: Include objective criteria for evaluating progress.
- Attainable: Realistic within the patient’s abilities and circumstances.
- Relevant: Aligned with the patient’s overall goals and values.
- Time-bound: Specify a timeframe for achieving the outcome.
- Nursing Interventions: These are the specific actions the nurse will take to address the identified nursing diagnoses and achieve the established goals. Interventions must be:
- Evidence-based: Grounded in research and best practices.
- Individualized: Tailored to the patient’s unique needs.
- Realistic: Feasible to implement within the healthcare setting.
- Clearly defined: Provide details on frequency, duration, and method.
- Specific: Include what the nurse will do, how, and when.
- Evaluations: This is the critical process of assessing whether the nursing interventions were effective in achieving the planned goals. This involves:
- Continuous monitoring: Regularly reassessing the patient’s condition.
- Comparing outcomes to goals: Analyzing if the patient is progressing as expected.
- Documenting evaluation: Clearly recording findings and any necessary modifications to the plan.
- Modifying the plan: If the interventions are not effective, adjusting goals, interventions, or diagnoses as needed.

Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Nursing Care Plan
Now that we understand the key components of a nursing care plan, let’s delve into the step-by-step process of creating one:
- Gather Comprehensive Assessment Data: This is the initial and most important step. Collect both objective data (vital signs, lab results) and subjective data (patient’s report of symptoms, concerns). Use a holistic approach, assessing all aspects of the patient’s well-being.
- Analyze the Assessment Data: Identify patterns, trends, and potential problems from the assessment data you’ve gathered. Look for areas where the patient is not meeting their health needs or where risks are present.
- Formulate Nursing Diagnoses: Based on your analysis, develop nursing diagnoses using standardized language. Make sure you understand the ‘related to’ factor. For example, “Impaired Physical Mobility related to pain.”
- Prioritize Nursing Diagnoses: Determine which nursing diagnoses are most critical and need immediate attention. Life-threatening situations always take precedence.
- Establish Patient-Centered Goals and Outcomes: Set clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Make sure they align with the patient’s specific needs and preferences.
- Plan Nursing Interventions: Choose evidence-based, individualized interventions that align with the patient’s nursing diagnoses and desired outcomes. Be specific and clear about the interventions.
- Implement Nursing Interventions: Carry out the planned interventions. Ensure proper documentation.
- Evaluate the Effectiveness of Interventions: Continuously monitor the patient’s progress and compare the actual outcomes with the planned goals. Did you achieve what you planned?
- Modify the Nursing Care Plan: If the goals are not met or the situation changes, modify the nursing care plan accordingly. This may require revisiting earlier steps and making necessary adjustments.
- Communicate with Healthcare Team: Share the plan with other members of the care team so they are aware of the goals, strategies, and progress.
Tips for Writing a Stellar Nursing Care Plan
Creating exceptional nursing care plans is not just about following steps; it’s about applying critical thinking and a patient-centered approach. Here are some tips:
- Think critically: Don’t just go through the motions; really understand the ‘why’ behind each aspect of your plan.
- Involve the patient: Include the patient in the planning process. Their input is vital to developing a patient-centered plan.
- Use evidence-based practices: Base your interventions on the best available research and guidelines.
- Be specific and measurable: Avoid vague goals and interventions.
- Be flexible: Plans should be adaptable to changes in the patient’s condition.
- Document thoroughly: Your plan should be clearly and accurately documented. This is essential for continuity and legal purposes.
- Seek mentorship and help: If you are struggling, don’t hesitate to ask for help with a nursing care plan from experienced colleagues.
- Utilize available resources: Take advantage of templates, software, and other resources that can streamline the planning process.
- Regularly review and update: A nursing care plan is a living document and should be updated according to the patient’s changing condition.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls to Avoid in a Nursing Care Plan
The nursing care plan is the cornerstone of effective patient care. It’s a dynamic, living document that outlines a patient’s specific needs, the goals of care, and the interventions required to achieve those goals. A well-constructed nursing care plan ensures consistency and promotes patient safety and positive outcomes. However, even experienced nurses can fall into common traps when developing these crucial documents. Understanding these pitfalls and knowing how to avoid them can significantly improve the quality of care provided.
Lack of Individualization
Perhaps the most frequent error is creating a generic nursing care plan that could apply to any patient with a similar diagnosis. This “cookie-cutter” approach ignores the unique circumstances of each individual, such as their age, culture, support system, and personal preferences.
- Pitfall: Using pre-printed templates without customizing them to the specific patient.
- Solution: Conduct a thorough assessment, focusing not just on the diagnosis, but also on the patient’s unique biopsychosocial needs. Document patient preferences and cultural considerations. Use these elements to craft individualized goals and interventions. The nursing care plan must reflect the person, not just the disease.
Vague or Unmeasurable Goals
A nursing care plan relies on clear, measurable goals. Vague objectives like “the patient will feel better” are not helpful because they don’t provide a way to assess progress or evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Pitfall: Using general language lacking quantifiable metrics.
- Solution: Employ SMART goals – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Instead of “patient will have less pain”, specify “patient will report a pain level of 3/10 or less within 30 minutes of pain medication administration.” This allows for objective evaluation and adjustment of the plan.
Inadequate Interventions
Interventions are the actions nurses take to help patients achieve their goals. Sometimes, the interventions listed in a nursing care plan are too general, superficial, or don’t align with the specific problem identified.
- Pitfall: Listing common interventions without tailoring them to the patient’s specific situation or needs.
- Solution: Ensure that interventions are based on evidence-based practice and are specific to the patient’s individual problem. Don’t just state “ambulate the patient”, but be specific as to the frequency and assistance required. Collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide a holistic plan. Critically evaluate the evidence behind each intervention and choose what is most likely to be beneficial.
Neglecting Patient and Family Involvement
The patient and their family should be active participants in the nursing care planning process. Their input is vital to setting realistic goals and selecting interventions that are acceptable and sustainable.
- Pitfall: Creating a plan without seeking input from the patient and their family, and therefore missing important contextual information.
- Solution: Actively engage patients and families in the goal-setting process. Explain the reason for each intervention, and encourage feedback. Recognize that their preferences and values are essential and should inform the plan. A well-informed patient is more likely to be engaged in their own recovery.
Failure to Update and Evaluate
A nursing care plan is not static. As a patient’s condition changes, the plan needs to be adjusted accordingly. Failure to regularly reassess the effectiveness of the nursing care plan can lead to ineffective interventions and delayed progress.
- Pitfall: Treating the initial nursing care plan as a static document, neglecting updates in response to changes in the patient’s health or progress.
- Solution: Implement a system for regular review and modification of the plan. Encourage feedback from all team members, including the patient and family. Use this feedback to revise the care plan, making it responsive to the patient’s evolving needs. This ensures the nursing care plan is always relevant and effective.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls and actively working to avoid them, nurses can create meaningful and effective nursing care plans that significantly improve patient outcomes. The nursing care plan serves as a roadmap, but also needs the flexibility to change when needed in response to the patient’s health journey.
The Importance of Nursing Care Plans in Different Settings
Whether you work in a hospital, clinic, long-term care facility, or even in a home health setting, the principles of a good nursing care plan remain the same. The structure and detail may vary based on the setting, but the core emphasis should always be on patient needs, individualized care, and the nursing process. A well-constructed plan ensures a unified approach among all care providers, which is particularly crucial in settings where continuity of care is paramount.
Seeking Nursing Care Plan Help
Sometimes, nurses may feel overwhelmed or uncertain when developing a nursing care plan. It’s perfectly normal to seek assistance and guidance. Asking for help is a sign of strength and commitment to providing the best possible patient care. If you are finding that you need nursing care plan help, don’t hesitate to seek out a mentor, a nursing instructor, or an experienced nurse who can offer support and insights.
Moving Beyond Templates: Customizing the Plan
While templates can be useful as a starting point, it’s vital to remember that each patient is unique. A good plan will reflect that individuality. Don’t rely solely on templates; focus on developing a plan that truly addresses the specific needs and concerns of your patient. Consider factors like their cultural background, personal beliefs, and family dynamics. This customized approach will result in a more effective and patient-centered healthcare plan.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Care Plans
Nursing care plans are fundamental to providing high-quality, patient-centered care. They act as a roadmap for nurses, guiding them in their daily tasks and ensuring consistency in care delivery. However, both new and experienced healthcare professionals often have questions about these essential documents. Let’s delve into some common queries:
What Exactly Is a Nursing Care Plan?
At its core, a nursing care plan is a formal document that outlines a patient’s health problems, the nursing interventions needed to address those problems, and the expected outcomes. It’s created collaboratively, often involving the patient, their family, and other healthcare team members. It’s more than just a list of tasks; it’s a thoughtful process that individualizes care to meet the unique needs of each person.
Why is a Nursing Care Plan Important?
A nursing care plan serves several critical purposes:
- Communication: It ensures everyone involved in the patient’s care is on the same page. This helps avoid confusion and duplication of effort.
- Consistency: It promotes consistent, evidence-based care, regardless of which nurse is on duty.
- Accountability: It provides a record of the care that’s been planned and delivered, ensuring accountability and facilitating audits.
- Patient-centered approach: By detailing patient-specific needs, it guides nurses in delivering care that’s tailored to the individual, enhancing their overall experience and well-being.
- Legal document: In some instances, the nursing care plan can serve as a legal record.

Who Creates the Nursing Care Plan?
The primary responsibility for creating a nursing care plan lies with the registered nurse (RN). However, it’s a collaborative process, and input from other healthcare team members like licensed practical nurses (LPNs), nursing assistants, therapists, and physicians is essential. It’s also crucial that the patient, when possible, actively participate in the development and ongoing adjustment of the plan.
How Often is a Nursing Care Plan Updated?
The plan should be reviewed and updated regularly. The frequency depends on the patient’s condition, but generally, it’s updated with each shift, after significant changes in the patient’s status, or when goals are achieved and new ones are set. A nursing care plan is not a static document; it evolves along with the patient’s needs.
What Happens if the Care Plan Isn’t Followed?
Failure to follow a care plan can lead to inconsistencies in care, negatively affecting patient outcomes. In a worst-case scenario, it could result in preventable complications, impacting a patient’s health and recovery. Nurses are professionally and ethically bound to follow the documented plan, but should also use their clinical judgement to make appropriate adjustments if necessary. It is essential for nurses to accurately document any deviations from the plan and why those were made.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of writing stellar nursing care plans is essential for providing the highest quality of patient care. These plans are more than just paperwork; they are a critical tool for guiding nursing practice, ensuring consistency, and achieving optimal health outcomes. By understanding the fundamental principles and engaging in the step-by-step process, you can create effective, patient-centered plans that truly make a difference. Remember to approach every plan with critical thinking, flexibility, and a genuine commitment to your patient’s well-being.
And if you’re struggling, don’t hesitate to seek resources and support, as building your skills in this area will contribute significantly to your success as a nursing professional. The impact of a well-crafted nursing care plan can be immeasurable, directly contributing to positive patient experiences and improved health results. And always remember that a patient-centered nursing care plan is key, not just the paperwork of the plan.
Get Professional Help with Nursing Care Plan Writing
At PhD Nurse Writer, we help students with writing original nursing papers. We can assist you to craft an authentic nursing care plan that sets you up for academic and professional excellence. Our service covers paper writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. We can also help you with nursing research papers, case studies, dissertations and essays.





