
Table of Contents
Nursing research plays a crucial role in advancing the science of nursing practice, improving patient care, and shaping healthcare policy. It’s through robust and rigorous research that we uncover new insights, test existing practices, and ultimately, build a stronger foundation for evidence-based care. A well-written nursing research methodology serves as the bedrock of any impactful study. It outlines the blueprint for how the research will be conducted, ensuring transparency, reproducibility, and ultimately, the credibility of the findings.
This article delves into the essential guidelines for crafting a compelling and comprehensive nursing research methodology section, providing clarity and direction for aspiring and seasoned researchers alike.
The Essence of Nursing Research Methodology
The essence of a nursing research methodology lies in its rigorous, systematic approach to investigating and understanding nursing phenomena in order to improve patient care and advance the profession. It’s about asking important questions, collecting and analyzing data ethically and effectively, and translating findings into actionable insights.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
1. Focus on Nursing-Relevant Issues:
Nursing research aims to address issues that are directly relevant to nursing practice, patient care, and the nursing profession. This includes investigating:
- Patient outcomes
- Nursing interventions and their effectiveness
- Patient experiences and perspectives
- Health disparities and inequities
- Nursing education and professional development
2. Employs a Variety of Research Approaches:
Nursing research embraces a wide range of methodologies, including:
- Quantitative: Utilizes numerical data and statistical analysis to measure and quantify phenomena.
- Qualitative: Explores subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives through interviews, focus groups, and observations.
- Mixed Methods: Combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
3. Emphasizes Rigor and Scientific Principles:
Nursing research adheres to rigorous scientific principles to ensure the validity and reliability of findings. This includes:
- Formulating clear research questions: Defining the scope and purpose of the study.
- Developing a systematic research plan: Outlining the methodology, data collection, and analysis procedures.
- Using appropriate data collection techniques: Selecting methods that are suitable for the research question and population.
- Analyzing data objectively and systematically: Employing appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques.
- Drawing valid conclusions: Interpreting findings within the context of the study and limitations.
4. Promotes Ethical Conduct:
Nursing research prioritizes the ethical treatment of participants and upholds ethical principles like informed consent, confidentiality, and beneficence.
5. Seeks to Translate Findings into Practice:
The ultimate goal of nursing research is to improve patient care and advance the nursing profession. This means:
- Disseminating findings: Sharing research results through publications, presentations, and other channels.
- Implementing evidence-based practices: Integrating research findings into clinical practice guidelines and decision-making.
- Advocating for policy changes: Using research findings to influence healthcare policies and improve patient care.
In essence, nursing research methodology provides a framework for generating credible and impactful knowledge that can shape the future of nursing practice and enhance the quality of care provided to patients.
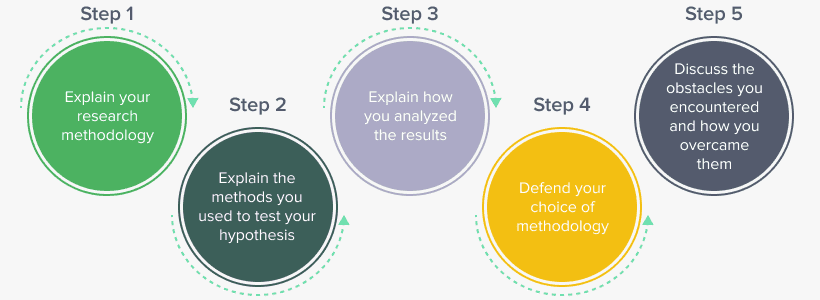
Steps to Crafting a Stellar Nursing Research Methodology
1. Defining the Research Question and Objectives:
The nursing research methodology should always begin with a clear articulation of the research question and objectives. These guide the entire research process, ensuring the study stays focused and relevant.
- Research Question: This is the central inquiry the study aims to answer. It should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, “Does the implementation of a patient education program improve adherence to medication regimens in patients with chronic heart failure?”
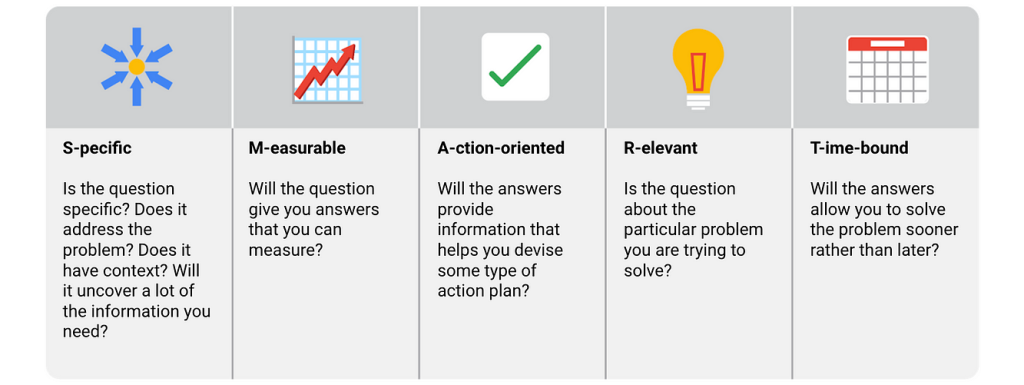
- Objectives: These are specific, measurable statements outlining the steps needed to answer the research question. Objectives should be aligned with the research question and provide a roadmap for achieving the study’s goals. For instance, an objective could be: “To assess the knowledge of medication management among patients with chronic heart failure before and after the implementation of the education program.”
2. Choosing the Appropriate Research Design:
The nursing research methodology must outline the research design selected to answer the research question. This choice is crucial, as it dictates the methods used for data collection and analysis. Common research designs in nursing include:
- Quantitative: This design utilizes numerical data to measure and quantify variables. Examples include:
- Experimental: This design involves manipulating an independent variable to observe its effect on a dependent variable. It’s often used to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Quasi-experimental: Similar to experimental design, but without random assignment of participants to groups. This is suitable when random assignment is not feasible or ethical.
- Correlational: This design examines the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating any of them. It aims to assess the strength and direction of the relationship.
- Descriptive: This design focuses on describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon. It uses surveys, interviews, or observations to collect data.
- Qualitative: This design explores subjective experiences, perspectives, and meanings. It utilizes non-numerical data, such as text, images, or videos, to gain deeper understanding. Examples include:
- Ethnography: This design investigates a culture or group’s shared beliefs, practices, and behaviors.
- Phenomenology: This design explores the lived experiences of individuals, seeking to understand their perceptions and interpretations of a phenomenon.
- Grounded theory: This design aims to develop a theory based on data collected from participants. It involves iterative cycles of data collection and analysis.
- Mixed Methods: This design combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the research question.
3. Selecting the Study Population and Sampling Techniques:
The nursing research methodology must clearly define the target population and the sampling method used to select participants. This ensures the findings can be generalized to the larger population.
- Target Population: This is the larger group the study aims to generalize its findings to.
- Sample: This is a subset of the target population selected for the study.
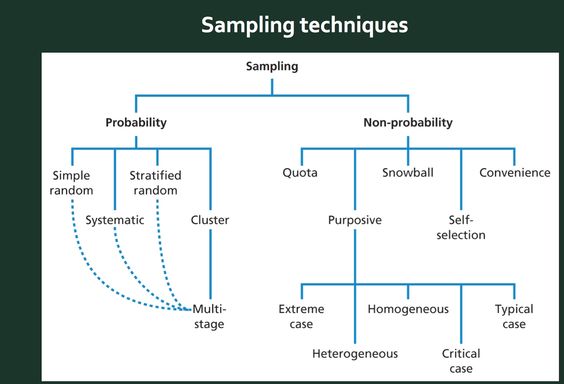
- Sampling Techniques:
- Probability sampling: Every member of the population has a known chance of being selected. Examples include:
- Simple random sampling: Each individual has an equal chance of being selected.
- Stratified random sampling: The population is divided into strata (e.g., age, gender), and participants are randomly selected from each stratum.
- Cluster sampling: The population is divided into clusters (e.g., schools, hospitals), and a random sample of clusters is selected.
- Non-probability sampling: The selection of participants is not based on chance. Examples include:
- Convenience sampling: Participants are selected based on their availability.
- Purposive sampling: Participants are selected based on their specific characteristics or knowledge.
- Snowball sampling: Participants are asked to refer other potential participants.
- Probability sampling: Every member of the population has a known chance of being selected. Examples include:
4. Data Collection Methods:
The nursing research methodology must describe the methods used to collect data, outlining the instruments, procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Instruments: These are the tools used to collect data, such as questionnaires, interviews, observations, physiological measures, or existing records.
- Procedures: These are the steps involved in collecting data using the selected instruments. For instance, a questionnaire might be administered online, in person, or via mail.
- Ethical Considerations: All research involving human subjects must adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring participant privacy, confidentiality, and informed consent.
5. Data Analysis Techniques:
The nursing research methodology should specify the methods used to analyze the collected data. This section should be tailored to the chosen research design and the type of data collected.
- Quantitative Data Analysis:
- Descriptive statistics: Used to summarize and describe the data. Examples include measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (standard deviation, range).
- Inferential statistics: Used to test hypotheses and draw conclusions about the population based on sample data. Examples include t-tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and regression analysis.
- Qualitative Data Analysis:
- Thematic analysis: Identifying patterns and themes within the data.
- Content analysis: Examining the content of text or images to identify patterns and themes.
- Grounded theory analysis: Developing a theory from the data collected.
- Mixed Methods Data Analysis: This involves integrating both quantitative and qualitative data. Different strategies exist, such as using quantitative data to inform the selection of participants for qualitative interviews.
6. Data Management and Security:
The nursing research methodology should describe how data will be managed, stored, and protected. This ensures the integrity and confidentiality of the data throughout the research process.
- Data Storage: Data should be stored securely, using appropriate methods like password-protected files, encrypted databases, or physical storage in locked cabinets.
- Data Security: Measures should be taken to prevent unauthorized access to and manipulation of the data, such as firewalls, access control protocols, and backup systems.
- Data Integrity: Procedures should be implemented to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data, including data entry checks, data cleaning processes, and regular data audits.
7. Pilot Testing and Refinement:
The nursing research methodology should discuss any pilot testing conducted to evaluate the instruments and procedures. This ensures the feasibility and effectiveness of the methods before implementation in the main study.
- Pilot Testing: This involves conducting a small-scale trial of the research methods to identify potential problems and make necessary adjustments before the main study.
- Refinement: Based on the findings from pilot testing, the research methods may be refined to improve their clarity, efficiency, and effectiveness.
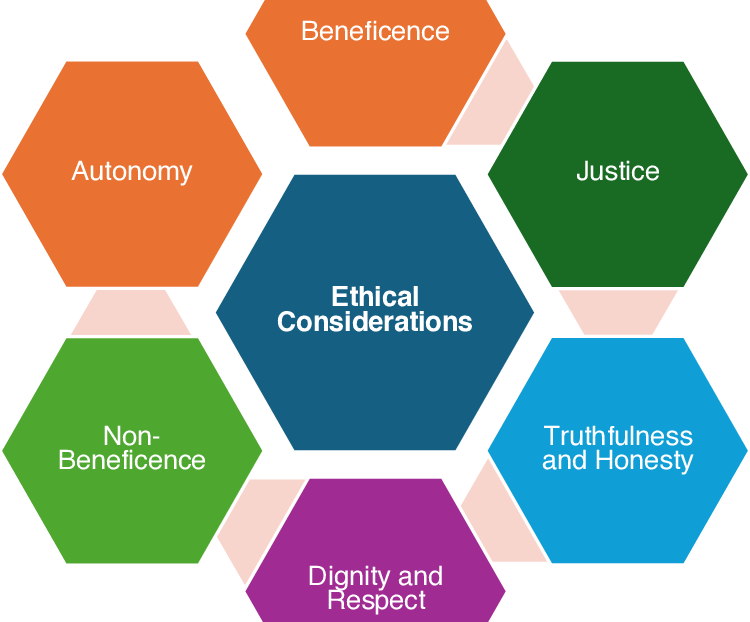
8. Ethical Considerations:
All nursing research methodology sections should explicitly address the ethical implications of the study, particularly when involving human subjects.
- Informed Consent: Participants must be informed about the study’s purpose, procedures, potential risks and benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Confidentiality: Participants’ identities and personal information must be protected, ensuring anonymity and confidentiality of data.
- Privacy: Researchers must respect the participants’ privacy and avoid intruding on their personal lives.
- Beneficence: The study should aim to maximize benefits for participants and minimize potential risks.
- Justice: The study should be conducted fairly, ensuring equitable selection of participants and distribution of benefits and risks.
- Institutional Review Board (IRB) Approval: All research involving human subjects must be reviewed and approved by an IRB, ensuring ethical guidelines are adhered to.
9. Dissemination of Findings:
The nursing research methodology should briefly outline how the findings will be disseminated to the relevant audience. This includes:
- Target Audience: This is the group the research findings are intended for, such as other researchers, clinicians, policymakers, or the general public.
- Dissemination Methods: This may include peer-reviewed publications in scholarly journals, presentations at conferences, or dissemination through professional networks or websites.
10. Limitations:
The nursing research methodology should acknowledge any limitations of the study, including factors that could potentially influence the findings or limit their generalizability. This demonstrates transparency and allows readers to interpret the findings within the context of the study’s limitations.
- Sample Size: A small sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings.
- Sampling Bias: If the sample is not representative of the target population, the findings may not be generalizable.
- Data Collection Methods: The reliability and validity of the data collection methods can influence the accuracy and reliability of the findings.
- Data Analysis Methods: The chosen data analysis methods may not be appropriate for all types of data or research questions.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Nursing Research Methodology
Writing a strong nursing research methodology is crucial for ensuring the validity and reliability of your research findings. Many pitfalls can lead to flawed results and hinder the impact of your study.
Here are some common mistakes in nursing research methodology and how to avoid them:
1. Lack of Clarity and Specificity:
- Mistake: Vague descriptions of methods or unclear explanations of procedures.
- Avoid: Ensure your nursing research methodology provides a precise, detailed account of all research methods, including data collection techniques, sampling procedures, and data analysis plans.
2. Inadequate Justification of Method Choice:
- Mistake: Not clearly explaining why you chose a particular methodology, leaving readers questioning its relevance.
- Avoid: Clearly justify your choice of nursing research methodology by aligning it with the research question, study aims, and the nature of the phenomenon under investigation.
3. Insufficient Attention to Ethical Considerations:
- Mistake: Failing to address ethical aspects, such as informed consent, data privacy, and potential risks to participants.
- Avoid: Thoroughly address ethical considerations in your nursing research methodology section, demonstrating adherence to ethical guidelines and protocols.
4. Unrealistic or Unfeasible Research Design:
- Mistake: Choosing a research design that is not practical given the time, resources, or scope of your study.
- Avoid: Select a nursing research methodology that is realistic and feasible, considering your available resources and time constraints.
5. Weak Data Analysis Plans:
- Mistake: Insufficiently describing the methods used for analyzing data, or failing to select appropriate statistical techniques.
- Avoid: Provide a detailed plan for data analysis in your nursing research methodology, outlining the specific statistical tools and approaches used to address the research questions.
6. Inadequate Literature Review:
- Mistake: Not thoroughly reviewing existing literature on the topic, leading to potential oversights or gaps in your methodology.
- Avoid: Conduct a comprehensive literature review to inform your nursing research methodology and ensure your approach is aligned with current research practices.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, you can strengthen your nursing research methodology and contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Research Methodology
- What is nursing research methodology?
Nursing research methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to investigate nursing phenomena and address critical questions relevant to the practice, education, and policy of nursing. - Why is nursing research methodology important?
Understanding nursing research methodology allows nurses to critically evaluate existing research, identify research gaps, and contribute to the development of evidence-based practices. - What are the different types of nursing research methodologies?
Common nursing research methodologies include quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods. Each approach utilizes different research strategies and data analysis techniques to answer specific research questions. - What are the ethical considerations in nursing research?
Ethical principles guide nursing research, including informed consent, confidentiality, and minimizing harm to participants. Understanding these principles is crucial for conducting ethical research. - How do I formulate a research question for my nursing research project?
A well-defined research question should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). It should clearly state the purpose and scope of your study. - How do I choose the appropriate research design for my nursing research project?
The choice of research design depends on the research question, the nature of the phenomenon under study, and the feasibility of the project. - How do I collect data for my nursing research project?
Data collection methods in nursing research vary depending on the research design, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, and physiological measurements. - How do I analyze data for my nursing research project?
Data analysis techniques depend on the type of data collected (quantitative, qualitative, or mixed). Common approaches include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, and content analysis. - How do I write up and disseminate the findings of my nursing research project?
Writing a research report involves clearly presenting the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions. Dissemination options include journal publications, conferences, and presentations. - Where can I find resources to learn more about nursing research methodology?
Numerous resources are available to assist nurses in their understanding of nursing research methodology. These include textbooks, online courses, research journals, and professional organizations like the Sigma Theta Tau International (STTI).
By understanding the basics of nursing research methodology, nurses can contribute to the advancement of the profession and improve patient care outcomes.
The nursing research methodology is the cornerstone of any research study. It ensures that the research is conducted rigorously, transparently, and ethically. By adhering to these guidelines, researchers can contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge, enhance patient care, and shape the future of healthcare. Writing a strong nursing research methodology not only sets the stage for a successful study but also strengthens the credibility of the findings, ensuring they contribute meaningfully to the body of knowledge in nursing practice.
Get Professional Nursing Research Methodology Writing Service
Crafting an outstanding nursing research methodology can be challenging even to seasoned writers. The easiest way to ensuring a compelling nursing research paper is through professional help from PhD Nurse Writer. We provide customized academic writing service for nursing research papers, essays, case studies and dissertations.





