
Table of Contents
The nursing profession stands as a cornerstone of healthcare systems worldwide. Nurses are at the forefront of patient care, navigating complex health challenges, technological advancements, and evolving patient expectations. As we look towards 2025, the landscape of healthcare continues its rapid transformation, demanding an equally dynamic and sophisticated approach to nursing care. Central to this evolution is the unwavering commitment to nursing best practices.
These practices represent the gold standard of care, integrating the best available evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to achieve optimal outcomes.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key nursing best practices essential for navigating the demands of nursing in 2025 and beyond.
Understanding nursing best practices is not merely an academic exercise; it is the bedrock upon which safe, effective, and compassionate care is built. They are not static rules but rather dynamic principles that adapt to new research, technological innovations, and the changing needs of diverse patient populations. Implementing and sustaining nursing best practices requires a continuous commitment from individual nurses, healthcare organizations, educators, and researchers.
Why Nursing Best Practices Must Evolve for 2025
The healthcare environment of 2025 is shaped by several significant trends, each influencing the application and definition of nursing best practices:
- Aging Population & Increased Complexity: Globally, populations are aging, leading to a higher prevalence of chronic diseases, comorbidities, and complex care needs. Nurses require advanced assessment skills, chronic disease management expertise, and proficiency in palliative and geriatric care.
- Technological Integration: Digital health technologies, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), telehealth platforms, remote patient monitoring, artificial intelligence (AI) for diagnostics, and robotic assistance, are becoming increasingly integrated into care delivery. Nursing best practices must incorporate digital literacy and the ethical use of these powerful tools.
- Focus on Health Equity and Social Determinants of Health (SDOH): There is growing recognition of the profound impact of social factors (e.g., socioeconomic status, education, environment) on health outcomes. Nurses are pivotal in identifying and addressing these determinants, advocating for vulnerable populations, and ensuring equitable access to care. Culturally competent care is a non-negotiable aspect of modern nursing best practices.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The proliferation of health data offers unprecedented opportunities to track outcomes, identify trends, and refine care processes. Nursing best practices increasingly rely on the ability to interpret data, participate in quality improvement initiatives, and contribute to evidence generation.
- Emphasis on Preventative Care and Wellness: Healthcare systems are shifting focus from solely treating illness to promoting health and preventing disease. Nurses play a crucial role in patient education, health coaching, and community health initiatives.
- Interprofessional Collaboration: Team-based care models are essential for managing complex patients. Effective communication and collaboration with physicians, therapists, pharmacists, social workers, and other professionals are fundamental nursing best practices.
Core Pillars of Nursing Best Practices
To meet the challenges and leverage the opportunities of the evolving healthcare landscape, nurses must ground their practice in several core pillars. These pillars represent the essential domains where nursing best practices are most critical.
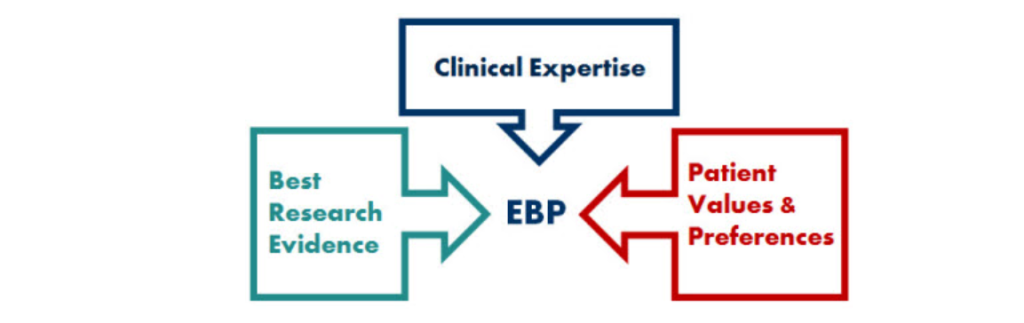
1. Evidence-Based Practice (EBP)
EBP remains the cornerstone of high-quality nursing care. It involves integrating the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient preferences and values when making clinical decisions.
- Key Components:
- Asking Clinical Questions: Formulating clear, answerable questions based on patient encounters (e.g., using the PICO format: Patient/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome).
- Acquiring Evidence: Efficiently searching relevant databases (e.g., PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library) for high-quality research studies.
- Appraising Evidence: Critically evaluating the validity, reliability, and applicability of the research findings.
- Applying Evidence: Integrating the appraised evidence with clinical judgment and patient context to guide care decisions and interventions.
- Assessing Outcomes: Evaluating the effectiveness of the practice change and identifying areas for further improvement.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: With the rapid generation of new research and data, EBP ensures that nurses are not relying on outdated or anecdotal information but are implementing interventions proven to be effective and safe. Adherence to EBP is a defining characteristic of nursing best practices.
2. Patient-Centered Care
This approach emphasizes partnership and respect, tailoring care to individual patient needs, preferences, and values. The patient is recognized as the expert in their own life and health.
- Key Components:
- Respect and Dignity: Valuing patient autonomy, choices, and cultural backgrounds.
- Information Sharing: Providing clear, unbiased information in an understandable format to empower patients.
- Participation and Collaboration: Encouraging patients and families to actively participate in care planning and decision-making.
- Emotional Support and Alleviation of Fear: Addressing patient anxieties and providing comfort and empathy.
- Coordination and Integration of Care: Ensuring smooth transitions and communication across different care settings and providers.
- Cultural Humility: Recognizing one’s own biases and actively seeking to understand and respect the diverse cultural perspectives of patients.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: Diverse populations, increased health literacy demands, and a focus on patient satisfaction necessitate a deeply ingrained patient-centered approach. It is fundamental to ethical and effective nursing best practices.
3. Safety and Quality Improvement (QI)
Patient safety is paramount. This involves minimizing the risk of harm through both system effectiveness and individual performance. QI is the systematic process of using data to improve care processes and outcomes.
- Key Components:
- Error Prevention: Implementing strategies to reduce medication errors, falls, healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), and pressure injuries (e.g., barcode scanning, checklists, bundles).
- Culture of Safety: Fostering an environment where staff feel comfortable reporting errors and near misses without fear of blame, allowing for system-level learning and improvement.
- Use of Technology: Leveraging EHR alerts, clinical decision support systems, and monitoring technologies to enhance safety.
- Standardized Procedures: Adhering to established protocols and guidelines for high-risk procedures and processes.
- Data Monitoring and Feedback: Regularly tracking safety metrics and QI initiatives to measure impact and guide further action.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: Complex care environments and increasing patient acuity heighten safety risks. A proactive, data-driven approach to safety and quality is inseparable from nursing best practices.
4. Effective Communication and Collaboration
Clear, timely, and respectful communication is vital for patient safety, care coordination, and positive team dynamics. This includes communication with patients, families, and other members of the healthcare team.
- Key Components:
- Therapeutic Communication: Using active listening, empathy, and clear language when interacting with patients and families.
- Interprofessional Communication: Utilizing standardized tools (e.g., SBAR: Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) for handovers and consultations. Respectful dialogue and shared decision-making within the team.
- Documentation: Maintaining accurate, comprehensive, and timely documentation in the EHR, which serves as a crucial communication tool.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing disagreements professionally and constructively.
- Utilizing Communication Technology: Employing secure messaging platforms and telehealth effectively for remote communication and collaboration.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: Team-based care models and the need for seamless care transitions make effective communication more critical than ever. It forms the connective tissue for implementing all other nursing best practices.
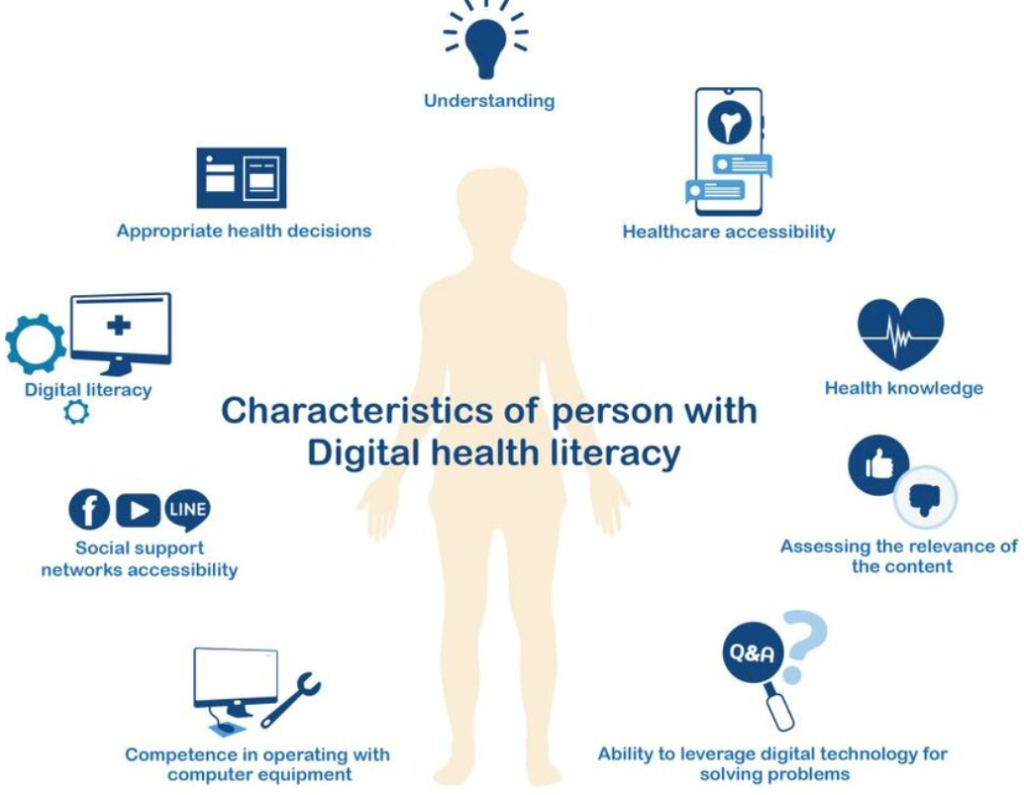
5. Technological Proficiency and Digital Health Literacy
Nurses in 2025 must be adept at using a wide range of health technologies safely and effectively. This goes beyond basic computer skills to include understanding data privacy, security, and the ethical implications of technology in care.
- Key Components:
- EHR Navigation and Utilization: Efficiently using electronic health records for documentation, order entry, medication administration, and accessing patient information.
- Telehealth Competency: Effectively conducting virtual visits, monitoring patients remotely, and troubleshooting basic technical issues.
- Data Interpretation: Understanding how to interpret data from monitoring devices, EHR dashboards, and quality reports.
- Ethical Use of Technology: Adhering to privacy regulations (e.g., HIPAA), ensuring data security, and considering the ethical implications of AI and algorithms in healthcare.
- Patient Education on Technology: Assisting patients in using patient portals, remote monitoring devices, or health apps.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: Technology is no longer peripheral but central to care delivery. Proficiency in this area is essential for efficiency, safety, and leveraging new tools to improve patient outcomes – a core component of modern nursing best practices.
6. Ethical Practice and Advocacy
Nursing is grounded in ethical principles. Nurses have a responsibility to act in the best interest of their patients, uphold professional standards, and advocate for patient rights.
- Key Components:
- Adherence to Code of Ethics: Understanding and applying principles like autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, fidelity, and veracity.
- Patient Advocacy: Speaking up for patient needs, preferences, and safety, especially for vulnerable individuals who cannot advocate for themselves.
- Informed Consent: Ensuring patients fully understand procedures, risks, benefits, and alternatives before giving consent.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: Protecting sensitive patient information.
- Navigating Ethical Dilemmas: Thoughtfully addressing complex situations involving conflicting values or resource allocation.
- Promoting Health Equity: Advocating for fair treatment and access to resources for all patients, regardless of background.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: Increasingly complex medical treatments, resource constraints, and societal inequities create challenging ethical scenarios. Strong ethical grounding and advocacy skills are fundamental nursing best practices.
7. Lifelong Learning and Professional Development
The rapid pace of change in healthcare necessitates a commitment to continuous learning throughout a nurse’s career.
- Key Components:
- Staying Current: Regularly reading professional journals, attending conferences, and participating in continuing education courses.
- Seeking Certification: Obtaining specialty certifications to demonstrate advanced knowledge and skills.
- Pursuing Advanced Degrees: Considering further education (e.g., BSN, MSN, DNP, PhD) to enhance expertise, leadership potential, or research skills.
- Mentorship: Seeking guidance from experienced nurses and mentoring newer colleagues.
- Reflective Practice: Regularly reflecting on experiences to identify learning needs and areas for improvement.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: Maintaining competence and adapting to new evidence, technologies, and care models is impossible without ongoing learning. It is essential for sustaining high standards of nursing best practices.
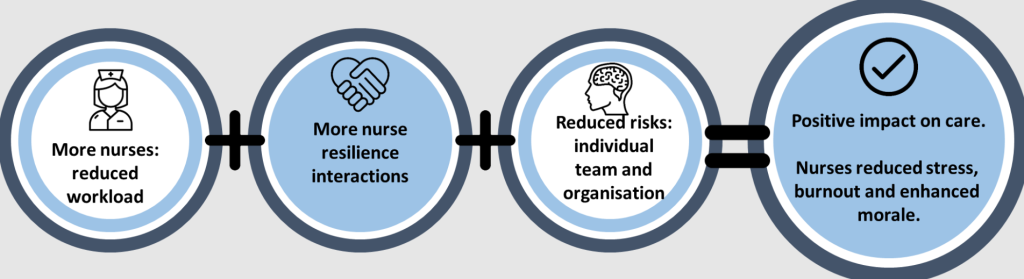
8. Nurse Well-being and Resilience
The demanding nature of nursing can lead to burnout, compassion fatigue, and moral distress. Protecting nurse well-being is not just beneficial for the nurse but essential for patient safety and the quality of care.
- Key Components:
- Self-Care Strategies: Prioritizing rest, nutrition, exercise, and stress management techniques.
- Setting Boundaries: Recognizing limits and avoiding overcommitment.
- Seeking Support: Utilizing peer support programs, employee assistance programs, and mental health resources.
- Organizational Support: Working in environments that promote manageable workloads, adequate staffing, respect, and access to resources.
- Building Resilience: Developing coping mechanisms to navigate stressful situations effectively.
- Why it’s Crucial for 2025: High levels of nurse burnout threaten the workforce and compromise patient care. Supporting nurse well-being is increasingly recognized as a critical organizational responsibility and a key factor in enabling consistent adherence to nursing best practices.
Implementing and Sustaining Nursing Best Practices
Adopting nursing best practices is an ongoing process requiring effort at multiple levels:
- Individual Nurse Level:
- Commitment to lifelong learning and EBP.
- Active participation in QI initiatives.
- Seeking feedback and engaging in reflective practice.
- Advocating for patient needs and safety.
- Prioritizing self-care and well-being.
- Organizational Level:
- Fostering a culture that values EBP, safety, and continuous improvement.
- Providing necessary resources: time for research, access to databases, adequate staffing, necessary technology.
- Offering ongoing education and training opportunities.
- Implementing supportive policies and procedures.
- Recognizing and rewarding adherence to nursing best practices.
- Strong nursing leadership that champions these principles.
- Educational Level:
- Integrating nursing best practices comprehensively into undergraduate and graduate curricula.
- Developing critical thinking, EBP, and QI skills in students.
- Emphasizing ethics, communication, and cultural humility.
The Role of Education, Research, and Academic Support
Nursing education plays a fundamental role in instilling the principles of nursing best practices from the outset. Curricula must evolve to equip future nurses with the knowledge and skills outlined above. Furthermore, nursing research is crucial for generating the evidence that underpins EBP and drives the refinement of nursing best practices.
Students often grapple with translating theoretical knowledge into practical application, particularly when documenting their understanding of complex concepts like EBP, QI models, or ethical frameworks in academic assignments. Understanding and articulating these nursing best practices is challenging. Some students, facing demanding coursework alongside clinical placements, may seek external resources. While exploring options like nursing paper writing services might seem appealing for structuring ideas, it’s crucial that students prioritize genuine learning and ethical conduct. Seeking help with nursing papers should focus on enhancing understanding and developing writing skills, perhaps through university writing centers or tutoring.
Ultimately, professional nursing paper help from PhD Nurse Writer seeks to guide students in mastering the material themselves, ensuring you can confidently apply nursing best practices in your future careers, rather than simply outsourcing the work. Our goal is comprehension and capability, not just task completion. We can help you with writing all types of nursing papers including research papers, term papers, essays, case studies, thesis and dissertations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Best Practices
Nursing is a dynamic field constantly evolving with new research, technologies, and patient needs. Central to providing high-quality, safe, and effective care is the concept of nursing best practices. But what does this term truly mean, and why is it so crucial? Here are answers to some frequently asked questions.
What Exactly Are Nursing Best Practices?
Nursing best practices refer to nursing care activities, interventions, or guidelines that are grounded in the best available evidence. This evidence typically comes from rigorous research, but best practices also integrate:
- Clinical Expertise: The nurse’s own knowledge and experience.
- Patient Values and Preferences: Ensuring care aligns with the individual patient’s needs, beliefs, and choices.
Essentially, they represent the most effective known methods for addressing specific clinical situations to achieve optimal patient outcomes. They are not static rules but evolve as new evidence emerges.
Why is Adhering to Nursing Best Practices So Important?
Following nursing best practices is fundamental for several reasons:
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Practices based on evidence are more likely to lead to positive health results, reduced complications, and faster recovery.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Best practices often incorporate safety protocols proven to reduce errors (e.g., medication administration, infection control).
- Standardized Care: They promote consistency and reduce variability in care quality across different nurses and settings.
- Increased Efficiency: Using proven methods can streamline care processes.
- Professional Accountability: Demonstrates a commitment to evidence-based care and professional standards.
How Can Nurses Stay Current with Best Practices?
The healthcare landscape changes rapidly, so continuous learning is vital. Nurses can stay updated on nursing best practices through various channels:
- Continuing Education (CE) Courses: Many courses focus specifically on evidence-based updates.
- Professional Journals: Publications like the American Journal of Nursing (AJN) or Journal of Nursing Scholarship regularly publish research and practice guidelines.
- Professional Organizations: Groups like the American Nurses Association (ANA) and specialty organizations often disseminate best practice guidelines.
- Evidence-Based Practice Resources: Utilizing databases (e.g., Cochrane Library, PubMed) and clinical practice guidelines repositories.
- Workplace Initiatives: Participating in quality improvement projects and unit-based education.
Understanding and consistently applying nursing best practices is essential for every nurse striving to provide excellent care. It requires a commitment to lifelong learning and integrating evidence into daily clinical decision-making, ultimately benefiting both patients and the nursing profession itself.
Conclusion: Embracing Excellence in 2025
Nursing in 2025 demands more than just technical skill; it requires critical thinking, adaptability, compassion, and an unwavering commitment to excellence. Nursing best practices provide the framework for achieving this excellence. By embracing Evidence-Based Practice, championing Patient-Centered Care, prioritizing Safety and Quality Improvement, mastering Communication and Collaboration, leveraging Technology effectively, upholding Ethical Principles, committing to Lifelong Learning, and nurturing Nurse Well-being, nurses can navigate the complexities of modern healthcare and provide the highest standard of care.
The journey towards optimal patient outcomes is continuous. Sustaining nursing best practices requires dedication from every nurse and robust support from healthcare organizations and educators. As the profession moves forward, a steadfast focus on these core principles will ensure that nursing remains a powerful force for health and healing in 2025 and for years to come. The consistent application of nursing best practices is not just a goal; it is the defining characteristic of professional nursing in the 21st century.





