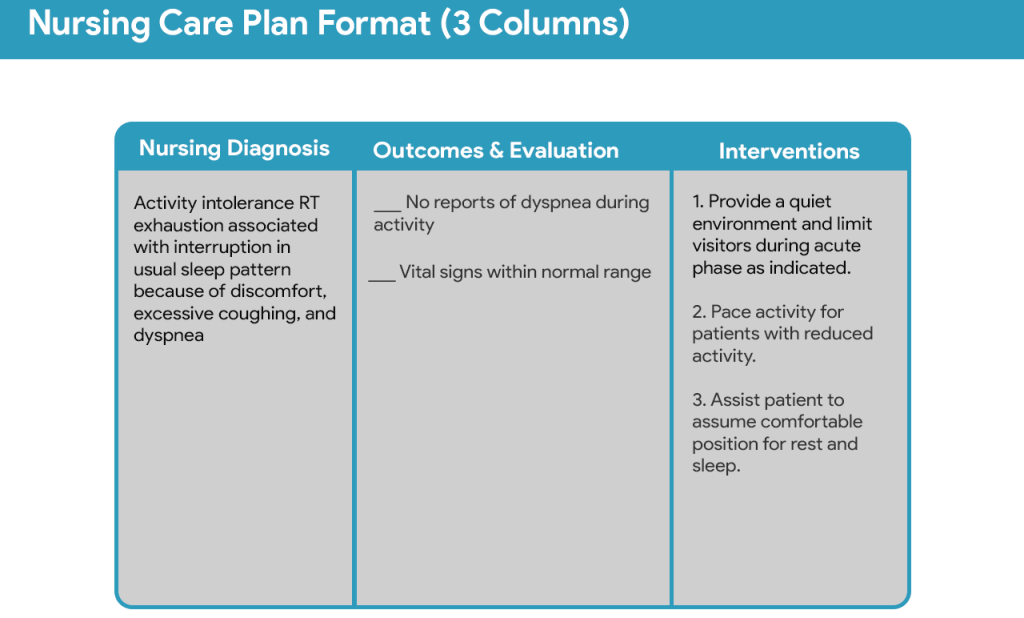
Table of Contents
The thought of tackling a nursing research paper can be daunting. With complex methodologies, demanding ethical considerations, and the pressure to contribute meaningfully to the field, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But fear not! A well-structured nursing research paper outline is your compass, guiding you through the labyrinth of research and ensuring a clear, compelling, and impactful final product.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of crafting a robust nursing research paper outline, providing you with the tools and strategies to navigate the research process with confidence.
Understanding the Importance of a Nursing Research Paper Outline
The nursing research paper outline serves as the blueprint for your entire research journey. It’s not just a skeletal framework; it’s a dynamic map that helps you:
- Clarify your research question: The outline forces you to articulate your research question with precision, ensuring it’s focused, relevant, and researchable.
- Organize your thoughts: The structure of the outline provides a logical framework for organizing your research findings, literature review, and methodology.
- Stay on track: By outlining the key sections, you establish a clear path, preventing you from getting lost in tangential information or overlooking crucial elements.
- Improve the flow and clarity of your writing: A well-structured outline ensures your paper flows seamlessly, with each section building upon the previous one, creating a cohesive narrative.
- Identify gaps in your research: The outlining process helps you identify potential areas where more research is needed or where additional information is required.
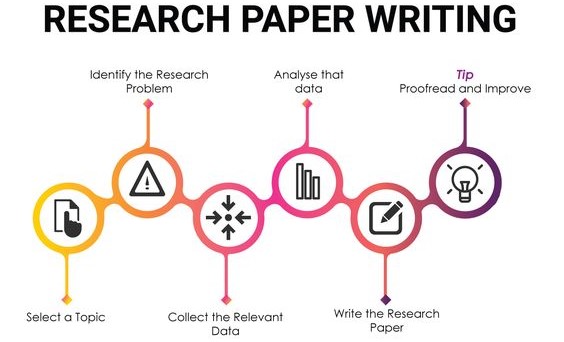
A Step-by-Step Guide to Crafting a Nursing Research Paper Outline
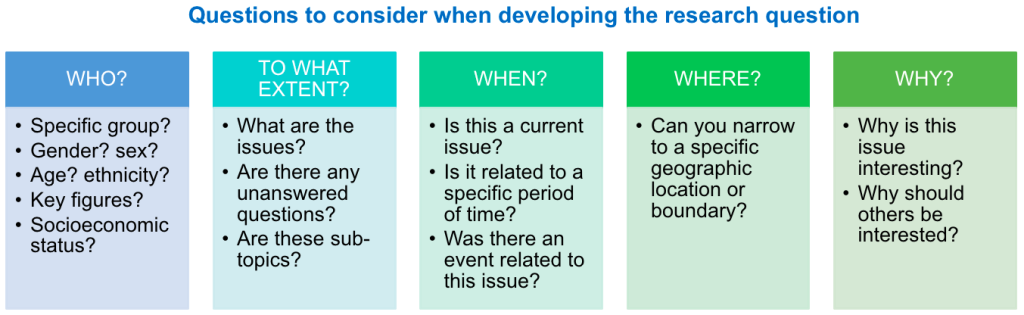
1. Define Your Research Question:
This is the foundation of your nursing research paper outline. Start by asking a clear, focused, and specific question that guides your entire research endeavor. This question should be relevant to the field of nursing, have potential for empirical investigation, and align with your area of interest.
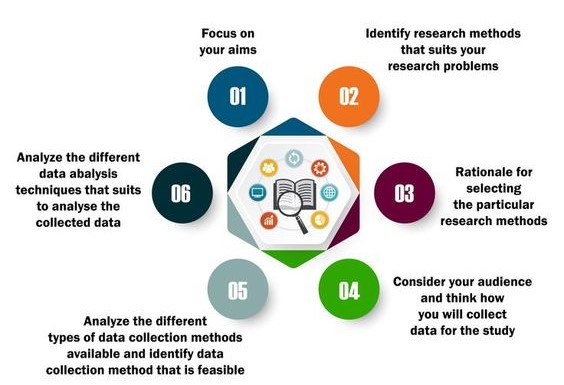
2. Conduct a Literature Review:
This crucial section involves examining existing research on your chosen topic. It’s essential for understanding the current state of knowledge, identifying gaps in the research, and shaping your research question.
- Identify Key Terms: Begin by identifying the key terms relevant to your research question. Use these terms to search databases like PubMed, Nursing Papers, CINAHL, and Cochrane Library.
- Organize your Findings: As you gather relevant research articles, organize them by theme, methodology, and findings. This will help you identify patterns, conflicting views, and potential areas for further investigation.
- Evaluate the Literature: Critically assess the quality and relevance of each article, considering factors like study design, sample size, and conclusions.
3. Develop Your Hypothesis or Research Aim:
Based on your research question and literature review, formulate a testable hypothesis or a specific research aim. This outlines the expected relationship between variables or the specific outcome you hope to achieve.
4. Choose a Research Design:
Select a research design that best suits your research question and hypothesis. This can range from quantitative designs like randomized controlled trials or quasi-experimental studies to qualitative designs like phenomenology or grounded theory.
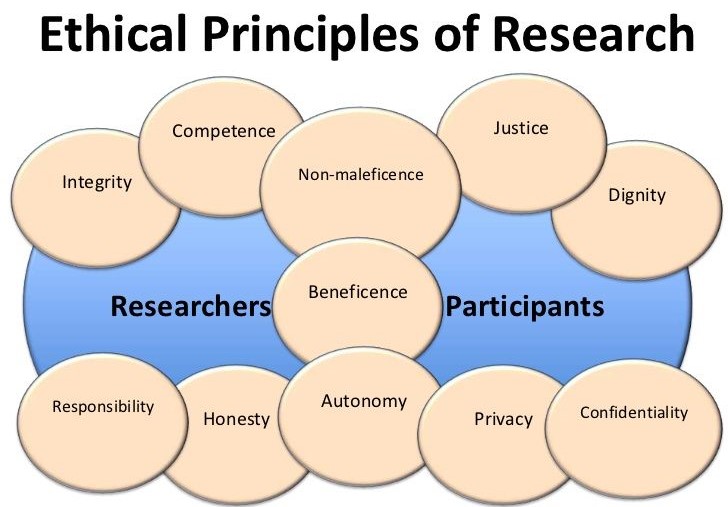
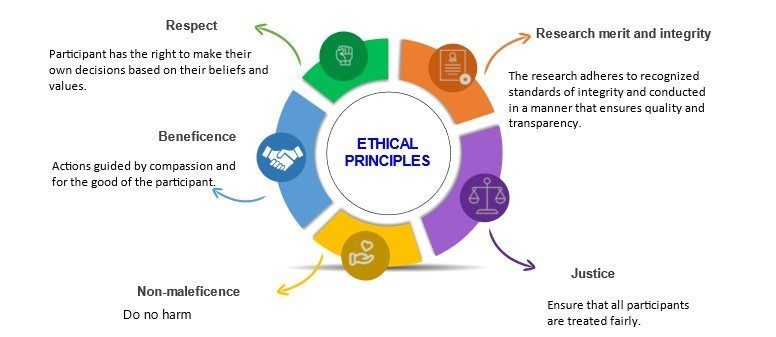
5. Establish Ethical Considerations:
Nursing research involves human subjects, making ethical considerations paramount. Ensure your research adheres to ethical guidelines, including informed consent, privacy, and confidentiality.
6. Determine Your Data Collection Methods:
Select data collection methods appropriate for your research design, including surveys, interviews, observation, or physiological measurements.
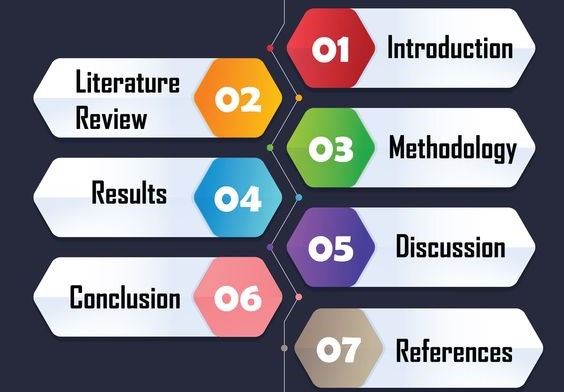
7. Outline the Structure of Your Nursing Research Paper Outline:
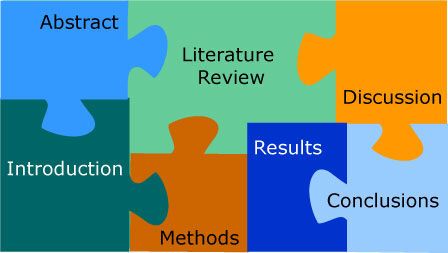
A typical nursing research paper outline includes the following sections:
a. Title Page:
- Include a concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of your paper.
- List your name, affiliation, and date.
b. Abstract:
- Provide a concise summary of your research paper, including the research question, hypothesis, methods, key findings, and conclusions.
- This section should be a self-contained overview that can be understood independently.
c. Introduction:
- Briefly introduce the topic and its significance.
- State your research question and hypothesis.
- Provide a brief overview of the relevant literature and its implications.
- Outline the purpose and significance of your study.
d. Literature Review:
- This section presents a comprehensive review of the existing literature relevant to your research question.
- Organize your findings thematically or chronologically.
- Highlight key findings and gaps in the literature.
- Analyze the existing research and connect it to your study.
e. Methods:
- Describe the research design, including the participants, setting, and data collection methods.
- Outline the procedures for data analysis.
- Explain how you ensured the ethical conduct of the research.
- Provide sufficient detail to allow for replication of your study.
f. Results:
- Present the findings of your research, using tables, figures, and descriptive statistics.
- Organize the results logically and provide clear explanations.
- Avoid drawing conclusions or interpreting the data in this section.
g. Discussion:
- Analyze and interpret the findings in light of your research question and hypothesis.
- Discuss the implications of your results, relating them to existing research and theoretical frameworks.
- Identify limitations of your study and suggest areas for future research.
h. Conclusion:
- Restate your research question and summarize your key findings.
- Discuss the significance of your findings and their implications for nursing practice, research, and policy.
- Briefly mention future research directions.
i. References:
- List all sources cited in your paper using a consistent formatting style, such as APA or AMA.
j. Appendices:
- Include any supplementary materials, such as questionnaires, data tables, or detailed protocols, that are not essential for the main body of the paper.

8. Writing the Nursing Research Paper Outline:
- Start with a rough draft: Initially, focus on creating a comprehensive, yet flexible outline, capturing the essence of each section.
- Use a hierarchical structure: Employ headings and subheadings to create a clear and organized structure, making your ideas easily accessible.
- Be specific and detailed: Provide brief but informative descriptions of the key points and arguments you plan to include in each section.
- Use bullet points and concise language: This makes your outline easily readable and facilitates a quick overview of your paper’s structure.
- Revise and refine: As you gather more information and refine your research, don’t hesitate to revise and refine your nursing research paper outline to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness.
9. Refining Your Nursing Research Paper Outline:
- Ensure logical flow: Check that the sections of your outline progress naturally, building upon each other to create a coherent narrative.
- Eliminate redundancy: Avoid repeating information unnecessarily. Ensure each section contributes uniquely to the overall purpose of your paper.
- Check for clarity and conciseness: Ensure that the language in your nursing research paper outline is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
- Seek feedback: Share your outline with peers, mentors, or faculty members for constructive criticism and suggestions.
10. Using the Nursing Research Paper Outline:
- Guide your research: Refer to your outline as you gather information, conduct data analysis, and write your paper.
- Stay organized: The outline keeps you focused, preventing you from going off-track and ensures you cover all necessary components.
- Streamline your writing process: A well-structured outline makes the writing process more efficient and less overwhelming.
Beyond the Outline: Essential Tips for Writing Compelling Research Papers
- Ensure your research is relevant and impactful: Choose a topic that addresses a significant issue in nursing practice and has the potential to improve patient care or advance the field.
- Use credible and relevant sources: Base your research on high-quality literature and evidence-based findings.
- Employ appropriate methodology: Select a research design and data collection methods that are aligned with your research question and hypothesis.
- Adhere to ethical guidelines: Ensure that your research respects the dignity and rights of participants, protects their privacy, and adheres to ethical principles.
- Clearly present your findings: Use tables, figures, and descriptive statistics to effectively communicate your results.
- Interpret your findings thoughtfully: Provide insightful and relevant interpretations of your data, connecting them to existing literature and theoretical frameworks.
- Acknowledge the limitations of your study: Be transparent about the limitations of your research, identifying any potential biases or shortcomings.
- Write clearly and concisely: Use clear and precise language to convey your message effectively.
- Proofread meticulously: Carefully check your paper for errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the Nursing Research Paper Outline
While a research paper outline is a valuable tool, it’s easy to make mistakes that can hinder the success of your final paper. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when writing your nursing research paper outline:
1. Vagueness and Lack of Specificity:
- Problem: Using vague or general terms in your outline can lead to a disjointed paper. For example, stating “Discuss the impact of stress on nurses” is too broad.
- Solution: Be specific and precise in your outline. Instead of “Discuss the impact of stress on nurses,” outline “Analyze the relationship between job burnout and medication errors among critical care nurses.”
2. Ignoring the Research Question:
- Problem: The outline should directly address your research question. If your outline doesn’t clearly connect to your main question, your paper may become disjointed and lose focus.
- Solution: Every section of your outline should relate back to your research question. Each point should contribute to answering the question or exploring its various aspects.
3. Insufficient Detail:
- Problem: A bare-bones outline with just headings and subheadings might seem efficient, but it can leave you lost when writing.
- Solution: Include brief but informative descriptions for each section, outlining the key points you plan to address, the arguments you’ll present, and the evidence you’ll use.
4. Lack of Flow and Logic:
- Problem: The outline should flow logically, with sections building upon each other. Skipping around or having unrelated sections will create a disjointed paper.
- Solution: Carefully consider the sequence of your sections. Ensure that the introduction leads logically into the literature review, followed by the methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
5. Overlooking Ethical Considerations:
- Problem: Ethical considerations are paramount in nursing research. Neglecting them in your outline can lead to significant problems in the paper’s design and execution.
- Solution: Include a dedicated section in your outline to discuss ethical considerations relevant to your research, including informed consent, privacy, confidentiality, and potential risks to participants.
6. Skipping the Literature Review:
- Problem: A strong literature review is crucial to establish the context and significance of your research. Neglecting it in your outline can lead to a weak paper.
- Solution: Dedicate a substantial section in your outline to the literature review. Outline the key themes, gaps in research, and relevant studies you plan to discuss.
7. Not Addressing Limitations:
- Problem: Every research study has limitations. Failing to acknowledge them in your outline can weaken your paper’s credibility.
- Solution: Include a section in your outline where you discuss the potential limitations of your research, such as sample size, sampling bias, or specific methodological challenges.
8. Leaving Out the Discussion Section:
- Problem: The discussion section is where you analyze your findings, connect them to existing literature, and interpret their significance. Skipping this section weakens your paper.
- Solution: Allocate a section in your outline specifically for the discussion. Outline the key findings, their implications, and how they relate to existing research.
9. Failing to Include References:
- Problem: Ignoring references in your outline can lead to plagiarism or inaccurate citations.
- Solution: Include a section for references in your outline. As you gather information, keep track of your sources and note them in your outline.
10. Lack of Revision and Refinement:
- Problem: A static outline that’s never updated or revised can hinder the progress of your paper.
- Solution: As you conduct research and gather information, revisit your outline and make necessary revisions to ensure it accurately reflects the content and direction of your paper.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can create a solid nursing research paper outline that sets the stage for a clear, well-structured, and impactful final paper. Remember, the outline is your roadmap, guiding you through the research process and ensuring a successful outcome.

Crafting a robust nursing research paper outline is an essential step toward writing a high-quality and impactful research paper. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can navigate the complexities of nursing research, effectively communicate your findings, and make a meaningful contribution to the field. Remember, the outline is not a rigid structure but a flexible tool that can evolve as your research progresses. So, embrace the process, use your outline as a guide, and let your passion for nursing research shine through!
Get Professional Nursing Research Paper Outline Help
Are you looking for help with writing a nursing research paper outline? Then, engage PhD Nurse Writer for professional research paper writing assistance. Besides a nursing research paper outline, we can also assist you with writing authentic nursing essays, case studies and dissertations.