Table of Contents
The emergency room (ER) is a crucible of human experience, a microcosm of the complexities and vulnerabilities inherent in life. For nurses, it’s a demanding, exhilarating, and often emotionally taxing environment. A dissertation on emergency room nursing offers a unique opportunity to delve into this critical area of healthcare, to uncover its intricate nuances, and to contribute meaningfully to the field.
This guide provides practical tips and insights for crafting a stellar dissertation on emergency room nursing, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to embark on this intellectually enriching and impactful journey.
What is Emergency Room Nursing?
Emergency room nursing is a specialized and demanding field of nursing that focuses on providing immediate and critical care to patients presenting with a wide range of medical emergencies. It’s a fast-paced, high-pressure environment that requires nurses to be highly skilled, adaptable, and capable of making quick, decisive decisions under pressure.
Here’s a breakdown of what emergency room nursing entails:
The Scope of Practice:
- Initial Assessment and Triage: ER nurses are the first point of contact for patients, performing a rapid assessment to determine the severity of their condition and prioritizing care based on urgency.
- Emergency Procedures: ER nurses assist physicians with a variety of emergency procedures, including intubation, wound care, IV insertion, and CPR.
- Medication Administration: They administer medications, monitor patients’ responses, and adjust dosages as needed.
- Patient Education and Support: ER nurses provide information and support to patients and their families, explaining diagnostic tests, treatment plans, and discharge instructions.
- Collaboration with Team Members: They work closely with other healthcare professionals, including physicians, paramedics, respiratory therapists, and social workers, to ensure seamless patient care.
- Documentation and Reporting: ER nurses meticulously document patient assessments, interventions, and responses, ensuring clear and accurate medical records.
Unique Challenges and Demands:
- High Patient Volume: ER nurses often manage a high volume of patients with diverse and complex medical needs, requiring efficient time management and prioritization skills.
- Time Pressure: The urgency of emergency situations demands quick thinking and decisive action, often with limited information and resources.
- Emotional Stress: ER nurses witness trauma, suffering, and loss, requiring strong emotional resilience and coping mechanisms.
- Shift Work and Irregular Schedules: ER nurses often work rotating shifts, including nights, weekends, and holidays, requiring flexibility and adaptability.
- Exposure to Infectious Diseases: ER nurses are at increased risk of exposure to contagious diseases, necessitating strict infection control measures.
Rewards and Benefits:
Despite the challenges, emergency room nursing offers several rewarding aspects:
- Making a Real Difference: ER nurses have the opportunity to provide immediate and life-saving care to patients in their most vulnerable moments.
- Fast-Paced and Dynamic Environment: The constant influx of diverse cases keeps the work exciting and intellectually stimulating.
- Developing Advanced Skills: ER nurses acquire a wide range of specialized skills, including advanced assessment, critical care, and emergency procedures.
- Continuous Learning and Growth: The dynamic nature of the ER fosters a culture of continuous learning and development.
- Strong Sense of Community: ER nurses work as a close-knit team, supporting each other through the demanding nature of the work.
Becoming an Emergency Room Nurse:
To become an emergency room nurse, you typically need:
- Registered Nurse (RN) License: This requires completion of a nursing program and passing the NCLEX-RN exam.
- Emergency Room Experience: Gaining experience in an ER setting can be acquired through internships, rotations, or entry-level positions.
- Continuing Education: ER nurses are encouraged to pursue certifications and specialized training in areas such as trauma care, critical care, or emergency medicine.
Emergency room nursing is a demanding but rewarding field that offers nurses a unique opportunity to make a significant impact on the lives of patients in their most critical moments.
How to Craft a Compelling Dissertation on Emergency Room Nursing
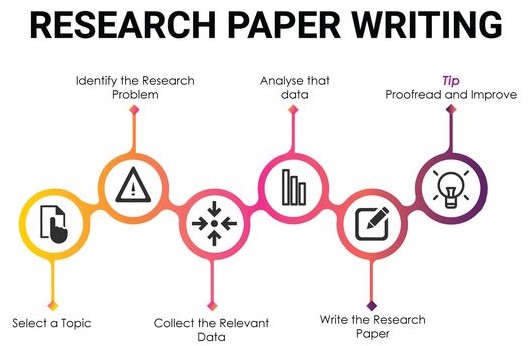
1. Choosing a Compelling Topic:
The first step in writing a compelling dissertation on emergency room nursing is selecting a topic that sparks your genuine interest and resonates with your personal experiences or professional goals.
Here are some avenues for inspiration:
- Clinical practice: Investigate the impact of specific nursing interventions on patient outcomes in the ER. For instance, you could explore the effectiveness of early mobilization protocols for stroke patients, the influence of pain management strategies on patient satisfaction, or the role of advanced practice nurses in managing complex trauma cases.
- Leadership and management: Examine leadership styles and organizational structures within the ER. You could analyze the impact of nurse-to-patient ratios on patient safety and staff satisfaction, explore the role of interprofessional collaboration in optimizing care delivery, or study the effectiveness of different nurse scheduling models.
- Patient experience: Focus on the unique challenges and perspectives of patients in the ER setting. This could involve investigating patient satisfaction with ER services, exploring the impact of wait times on patient anxiety, or examining the effectiveness of culturally sensitive communication strategies.
- Research and innovation: Explore new technologies, research methodologies, or emerging trends in emergency room nursing. You could assess the impact of telemedicine in ER care, investigate the feasibility of incorporating mobile health applications in patient education, or analyze the ethical implications of using artificial intelligence in decision-making.
Remember: Choose a topic that you find genuinely interesting and challenging. Your passion for the subject will fuel your research and writing, resulting in an engaging dissertation on emergency room nursing.
2. Conducting Rigorous Research:
A solid foundation of research is critical to writing a successful dissertation on emergency room nursing.
Here are some key steps to ensure your research is comprehensive and impactful:
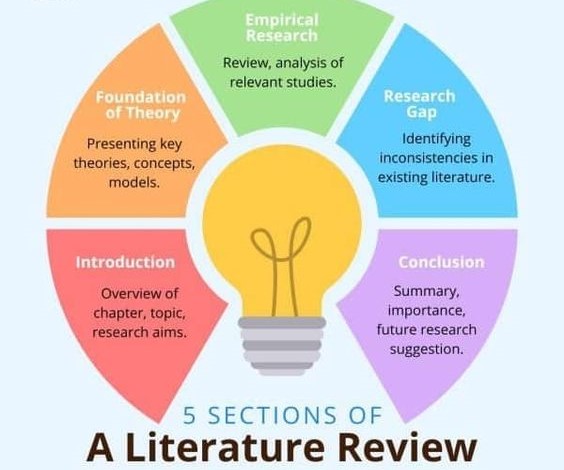
- Literature review: Delve into existing literature on your chosen topic, reviewing relevant studies, scholarly articles, and professional guidelines. This step will provide a deep understanding of the current state of knowledge, identify research gaps, and inform the direction of your own research.
- Data collection: Select appropriate methods to collect data for your dissertation. This could involve quantitative methods like surveys, experimental designs, or statistical analyses; qualitative methods like interviews, focus groups, or ethnographic observations; or mixed-methods approaches combining both quantitative and qualitative data.
- Data analysis: Analyze your collected data using appropriate statistical or qualitative techniques, ensuring a rigorous and objective approach. This step involves identifying patterns, trends, and relationships within your data, leading to valuable insights and conclusions.
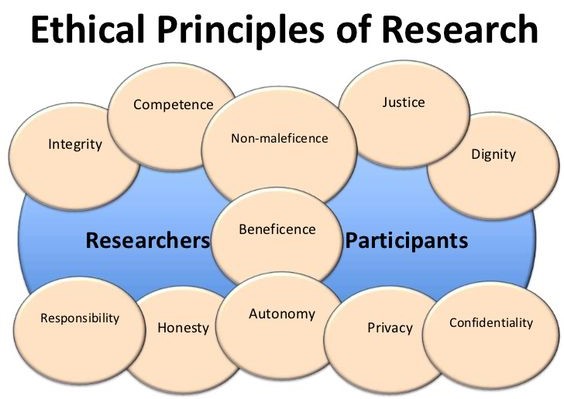
- Ethical considerations: Throughout the research process, uphold the highest ethical standards. Ensure informed consent from participants, protect patient confidentiality, and maintain data integrity.
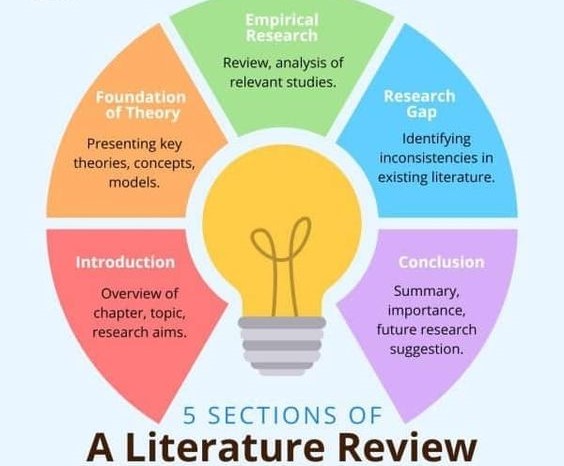
3. Structuring Your Dissertation on Emergency Room Nursing:
A well-structured dissertation on emergency room nursing provides a clear and compelling narrative, guiding the reader through your research and analysis.

Here’s a suggested structure:
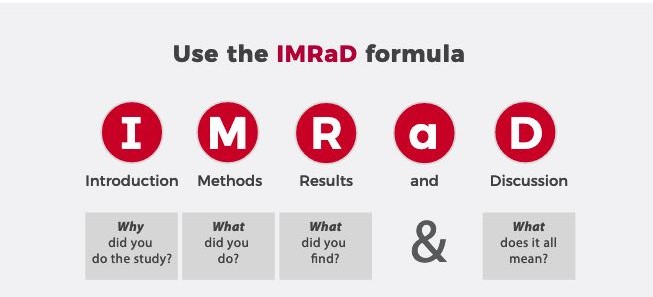
- Introduction: Introduce your topic, outline its significance, and state your research question(s) or hypothesis. This section should clearly articulate the purpose and scope of your dissertation on emergency room nursing.
- Literature review: Synthesize the existing literature on your chosen topic, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in knowledge. This section establishes your dissertation’s connection to the broader field of emergency room nursing.
- Methodology: Describe the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques used in your dissertation. This section ensures the transparency and replicability of your research.
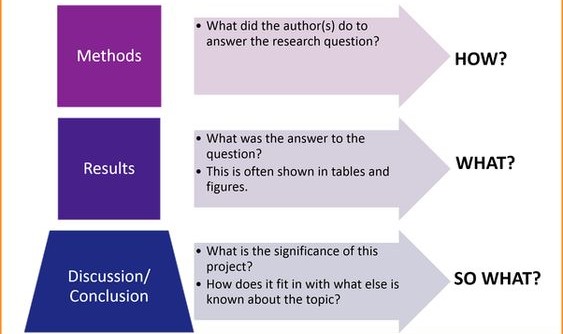
- Findings: Present your research findings in a clear and organized manner, using tables, graphs, or other visual aids as appropriate. This section showcases the results of your research on emergency room nursing.
- Discussion: Interpret and discuss the significance of your findings, relating them back to your research question(s) or hypothesis. This section connects your findings to the broader body of knowledge on emergency room nursing.
- Conclusion: Summarize your key findings, highlight the implications for practice and future research, and provide a concluding statement for your dissertation on emergency room nursing.
- References: List all cited sources in accordance with a specific style guide (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Appendices: Include any supporting materials, such as data collection instruments, interview transcripts, or statistical analyses.
4. Writing with Clarity and Precision:
Effective writing is crucial for a successful dissertation on emergency room nursing.
Here are some essential tips for writing a clear and precise dissertation on emergency room nursing.
- Active voice: Use active voice wherever possible, making your writing more engaging and concise.
- Concise language: Avoid jargon or overly technical language. Use plain language that is readily understandable to a broad audience.
- Logical flow: Structure your writing logically, using transitions to connect ideas and guide the reader through your arguments.
- Proofreading: Carefully proofread your dissertation for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. It is also beneficial to have colleagues or mentors review your work for clarity and accuracy.
5. Seeking Feedback and Guidance:
Throughout the dissertation process, seeking feedback from mentors, advisors, and colleagues is invaluable.
Here’s how to leverage feedback effectively for your dissertation on emergency room nursing.
- Identify trusted sources: Choose mentors and advisors who possess expertise in emergency room nursing and dissertation writing.
- Regular meetings: Schedule regular meetings with your advisor to discuss your progress, receive feedback on your research, and address any challenges.
- Peer review: Share your work with colleagues or peers for constructive feedback on your writing, research, and analysis.
- Open to criticism: Welcome feedback, even if it is critical, as it provides opportunities for improvement.
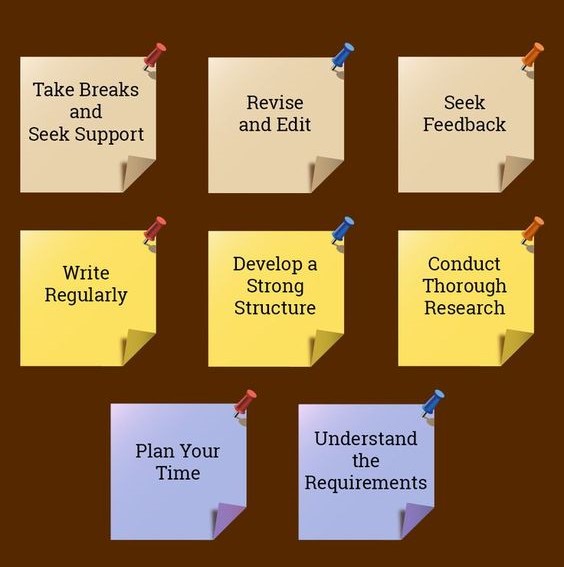
6. Embracing the Journey:
Writing a dissertation on emergency room nursing is a challenging but rewarding journey. It requires dedication, perseverance, and a willingness to learn and grow.
Here are some tips for navigating the journey:
- Set realistic goals: Break down the dissertation process into smaller, manageable tasks to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Manage time effectively: Create a writing schedule and stick to it as much as possible, prioritizing writing time over other commitments.
- Seek support: Lean on your mentors, advisors, and support network for guidance and encouragement.
- Celebrate milestones: Acknowledge your progress and achievements, reminding yourself of your commitment and resilience.
Potential Dissertation Topic Ideas on Emergency Room Nursing
Here are some specific topic ideas to inspire your dissertation on emergency room nursing:
- Examining the impact of electronic health records on medication administration errors in the emergency room.
- Assessing the effectiveness of pain management interventions for pediatric patients with acute appendicitis.
- Exploring the experiences of nurses who provide care to patients with mental health crises in the emergency room.
- Investigating the relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient outcomes in emergency room settings.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of nurse-led discharge planning for patients discharged from the emergency room.
- Analyzing the impact of cultural competency training on nurse communication with diverse patient populations.
- Assessing the feasibility of implementing a rapid assessment tool for identifying patients at risk for sepsis in the emergency room.
- Investigating the impact of workplace bullying on nurse job satisfaction and retention in emergency room settings.
- Exploring the use of simulation-based training to improve nurse skills and knowledge in emergency room procedures.
- Examining the role of nurse leaders in promoting a culture of safety within the emergency room.
A dissertation on emergency room nursing provides a unique opportunity to contribute meaningfully to the field of healthcare. By choosing a compelling topic, conducting rigorous research, and writing with clarity and precision, you can create an intellectually stimulating and impactful dissertation on emergency room nursing.
Remember, the journey may be challenging, but with dedication, perseverance, and the support of your mentors, you can craft a dissertation on emergency room nursing that leaves a lasting legacy in this critical nursing specialty.
Key Takeaway: A dissertation on emergency room nursing is an opportunity to explore critical issues, contribute to knowledge, and ultimately improve patient care. With meticulous planning, rigorous research, and effective writing, you can create a dissertation that is both valuable and impactful.
Get Professional Nursing Dissertation Writing Service
At PhD Nurse Writer, we offer a customized dissertation writing service that is tailored to your specific goals and aspirations. We can assist you with crafting a powerful dissertation on emergency room nursing and several other nursing specialties. Our service covers topic suggestion, dissertation writing, proof reading and editing, plagiarism check and removal. We guarantee stellar nursing dissertations, research papers, essays and case studies that will truly set you up for success.